Some of the best green energy alternatives include Solar Power, Bioorganic, Wind Power, and Geothermal power.
Imagine a world where the air is clean, nature thrives, and our energy is sourced from the powerful forces of the Earth itself. It sounds like a dream, doesn’t it? Well, it’s closer to reality than we might think!
Currently, most of our energy comes from burning fossil fuels like oil and coal. But these sources are not only harmful to our planet, they’re also running out. Fortunately, the future of power is changing, and it’s painted in shades of green, hence the focus on green energy alternatives.
In this post, we will journey through the exciting realm of green energy alternatives, the heroes of our sustainable future. We’ll explore how they work, their benefits, and the promising innovations.
So, whether you’re a curious individual, an aspiring environmentalist, or someone simply wanting to lower their electric bill, this article has something for you.
The Downfall of Fossil Fuels

When you turn on a light, start your car, or heat your home, there’s a good chance you’re using energy derived from fossil fuels. These are ancient carbon-based resources formed millions of years ago from the remains of plants and animals.
While fossil fuels have powered the modern world and fueled significant technological advances, their continued usage is now revealing severe drawbacks such as;
Air Pollution
One of the most immediate and noticeable impacts of burning fossil fuels is air pollution. Cities worldwide are blanketed in smog, a toxic cocktail of pollutants, largely due to vehicle exhaust and industrial emissions. This not only obscures skylines but also poses health risks.
Global Warming and Climate Change
Beyond the visible pollution lies a more insidious issue: the emission of greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2). These gases trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to global warming.
Rising temperatures have created a domino effect, causing melting polar ice caps, rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and disruptions to biodiversity.
Water and Soil Contamination
It’s not just the affected air. The extraction, refinement, and spills related to fossil fuels can contaminate water sources and soil. Oil spills in oceans, for instance, have devastating effects on marine life and ecosystems.
Dependence on Oil-Rich Nations
Many countries heavily rely on imports from oil-rich regions, leading to geopolitical tensions and trade imbalances. This dependence can make nations vulnerable to supply shocks and price fluctuations.
Finite Resources
By their very nature, fossil fuels are finite. We’re consuming them at a rate far faster than they were created, which further heightens the need for more green energy alternatives.
Some experts predict we could see significant oil shortages in the next few decades, and coal and natural gas are close behind.
Extraction Challenges
As the ‘easy-to-reach’ deposits are depleted, companies resort to more extreme methods to extract fossil fuels, like deep-sea drilling or fracking. These methods are not only more expensive but often come with increased environmental risks.
The Best Green Energy Alternatives
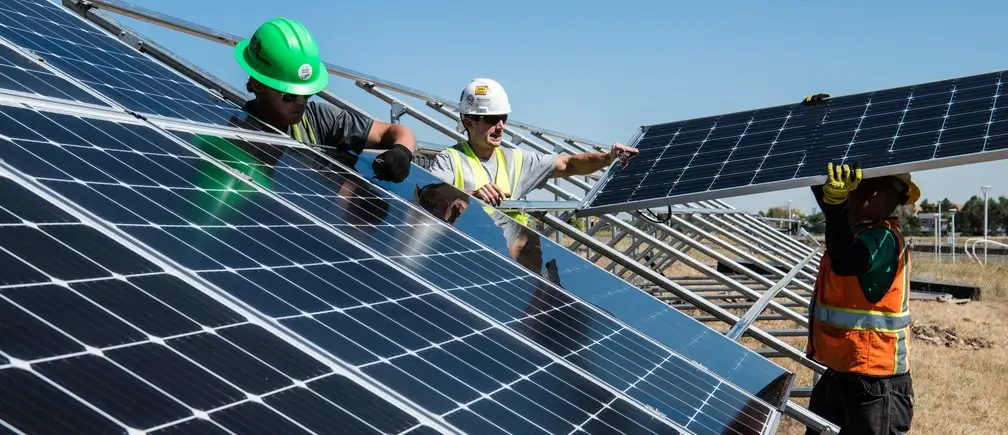

1. Solar Energy: Harnessing the Power of the Sun
The sun has been a source of light and life for our planet for billions of years. But only in the past few decades have we truly started tapping into its immense power to generate electricity.
Solar energy, put simply, involves converting sunlight directly into electricity. And if you think about it, the sun generously offers a staggering amount of energy – enough to power the entire world many times over if we could capture it all, and that makes it one of the best green energy alternatives.
How Does It Work?
Solar power is generated using panels made up of cells, usually silicon-based, known as photovoltaic (PV) cells. When sunlight strikes these cells, it excites electrons, causing them to move and generate electricity.
This direct conversion of sunlight to electricity happens without any moving parts, noise, or emissions. It’s like having a silent power plant right on your roof!
Benefits of Solar Energy
Abundance: The sun shines almost daily in many parts of the world, offering a consistent and limitless power source.
Decreasing Costs: Remember when the first mobile phones came out, and they were bulky and super expensive? Over time, they became sleeker, more efficient, and affordable.
The same is happening with solar panels. Thanks to technological advancements and increased demand, the cost of solar installations has plummeted over the years.
Sustainability: Solar panels can last for 25 to 30 years with minimal maintenance. Once installed, they keep generating free electricity for years to come.
Environmental Impact: Solar panels produce electricity without emitting greenhouse gases. By switching to solar, we reduce our carbon footprint and help combat climate change.
Economic Savings: Once the initial setup costs are covered, solar systems can significantly reduce or even eliminate electricity bills.
In addition, many governments offer incentives or tax breaks for those who install solar panels, further reducing the overall cost.
Real-World Applications
Residential Rooftop Systems: Many homeowners are turning their rooftops into mini power plants. These systems can be tailored to meet the energy needs of a household.
Solar Farms: These are large-scale installations of solar panels, often spanning acres of land. They function like traditional power plants but derive energy solely from the sun.
Solar-Powered Devices: From calculators to street lamps and even charging stations, small-scale solar applications are becoming ubiquitous.
Community Solar Projects: For those who don’t have the means or the ideal location to install their own solar panels, community solar projects allow multiple people to benefit from a shared solar grid.
2. Wind Energy: Riding the Breezes
When we think of wind, we might envision a gentle breeze on a warm day or the powerful gusts that precede a storm.
But have you ever considered the immense power wind holds and its potential to light up our cities, run our factories, and charge our phones?
This is where wind energy comes into play – an ancient force harnessed in innovative ways to power our modern world.
The Mechanics of Wind Turbines
At the heart of wind energy are wind turbines, towering structures with blades that capture wind’s kinetic energy. But how exactly do these giant fans convert a gust of wind into electricity? It starts with the blades.
As the wind blows, it creates lift, much like the wings of an airplane, causing the blades to turn. These blades are connected to a rotor, which in turn spins a generator inside the turbine.
The generator is the magical box where the real transformation occurs, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy that can then be fed into the power grid or used directly.
The design of wind turbines has evolved significantly over the years. Today’s turbines are taller, with longer blades and more efficient designs, allowing them to capture even the slightest breeze.
Innovations like offshore wind farms, where turbines are installed in the sea, take advantage of stronger and more consistent winds. Vertical-axis turbines, a newer design, can capture wind from any direction and could revolutionize how we think about wind energy in urban environments.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Wind energy is a true champion when it comes to environmental benefits. It’s a clean source of power and one of the best green energy alternatives.
Moreover, wind farms, whether on land or at sea, can coexist with local agriculture and marine life, often with minimal impact.
Economically, the wind industry has become a powerhouse of job creation and investment. As the technology has matured, costs have plummeted, making wind energy one of the most competitive forms of renewable energy on the market today.
Rural areas, in particular, have benefited, with farmers and landowners hosting turbines on their land and receiving rent payments in return.
Countries around the world are riding the winds of change. For instance, Denmark generates more than 40% of its electricity from wind and plans to increase this even further.
In the United States, states like Texas, Iowa, and Oklahoma have become leaders in wind energy, with sprawling wind farms dotting their landscapes.
Offshore wind farms are also gaining traction. The United Kingdom boasts the world’s largest offshore wind farm, Hornsea One, with enough capacity to power well over a million homes.
China, too, is rapidly expanding its wind energy capacity, both onshore and offshore, recognising the strategic importance of this renewable resource.
3. Hydropower: The Strength of Flowing Water

Water has shaped our landscapes, carved our valleys, and sustained life throughout history. But beyond its vital role in our ecology and communities, water is a profound source of power and one of the best green energy alternatives.
Civilisations have harnessed their force across time, and today, with technological advancements, we are transforming the kinetic energy of flowing water into clean electricity.
Understanding the Potential of Water Currents
When you observe a swiftly flowing river or a cascading waterfall, you’re witnessing the kinetic energy inherent in moving water. This energy, when channeled and directed with purpose, offers the potential to generate electricity.
Types of Hydropower
Various methods enable us to capture the energy of water:
- Dams: These are perhaps the most iconic representations of hydropower. Dams are built across large rivers to store water in reservoirs. When this stored water is strategically released, it flows through turbines, generating electricity. Iconic structures like the Hoover Dam stand testament to this engineering marvel.
- Tidal Power: The Earth and the Moon’s gravitational interplay results in the rhythmic ebb and flow of ocean tides. Tidal power systems are designed to harness the energy from these movements. As tides surge in and out, water flows through turbines in specialized underwater stations or barrage setups, creating electricity.
- Run-of-the-River: Unlike large-scale dam projects, run-of-the-river systems don’t rely on significant water storage. Instead, they utilize a segment of a river’s natural flow.
This water is channeled through a pipeline or diversion, passing through turbines and then seamlessly rejoining the river downstream.
These systems have a lighter touch on the environment since they maintain much of the river’s natural state.
4. Geothermal Energy: Earth’s Hidden Power
Beneath our feet lies a powerhouse so vast and potent that it has the capability to meet our energy needs many times over.
This is the power of the Earth’s core, a simmering cauldron of heat generated by the decay of radioactive materials and the residual heat from the planet’s formation.
Geothermal energy seeks to tap into this immense reservoir of thermal energy, presenting an exciting, reliable, and often overlooked pillar in the pantheon of green energy alternatives.
The journey of geothermal energy begins deep within the Earth. Here, heat from the planet’s core continuously flows outward, warming the surrounding rock and water.
In some areas, this heat is more accessible due to geological factors, such as volcanic activity or hot springs. It’s in these geothermal hotspots that we can most effectively harness this power.
The Process: How We Capture Geothermal Energy
Harnessing geothermal energy typically involves drilling wells into these geothermal reservoirs, allowing the hot water and steam trapped beneath the surface to rise. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
- Drilling and Extraction: Wells are drilled into the Earth to reach reservoirs of hot water and steam.
- Heat Transfer: The extracted heat is then transferred to a fluid, usually water or a refrigerant.
- Power Generation: This heated fluid is used to turn turbines, which in turn generate electricity.
- Reinjection: Finally, the cooled fluid is often reinjected back into the Earth, maintaining the pressure of the reservoir.
The Benefits of Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is brimming with advantages:
- Reliability: Unlike solar or wind power, geothermal energy isn’t subject to the whims of the weather. The Earth’s heat is constant and predictable.
- Efficiency: Geothermal power plants can operate 24/7 with high efficiency, regardless of external conditions.
- Low Emissions: While not entirely emission-free, geothermal energy has a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels.
- Land Footprint: Geothermal plants typically require less land per megawatt than many other energy sources.
- Economic Stability: Geothermal energy isn’t subject to the market fluctuations associated with fuel-based energy, leading to more stable energy prices.
Geothermal Energy Around the World
Several countries have tapped into their geothermal potential with significant success. For instance, Iceland meets nearly 30% of its electricity needs and 90% of its household heating through geothermal sources.
The United States is the world’s largest producer of geothermal energy, with the largest geothermal plant located in California’s Geysers Geothermal Complex.
Countries like Indonesia, the Philippines, and New Zealand also make substantial use of their geothermal resources.
5. Bioenergy: Organic Solutions for Power Needs
When we think of energy sources, vast oil fields or massive solar farms might come to mind. But what if I told you that the waste you throw away, the crops grown in fields, or even the leftovers from your dinner could be transformed into an amazing green energy alternative?
That’s the magic of bioenergy, an age-old energy solution now seeing innovative modern applications.
Understanding Bioenergy
At its core, bioenergy is energy derived from organic materials, commonly referred to as biomass. This biomass can be anything from agricultural residues, like straw and manure, to specially grown energy crops, like willow or switchgrass.
When these materials decompose, burn, or undergo certain treatments, they release energy in the form of heat or biofuels, which can then be used for heating, electricity, or even transportation.
Types of Bioenergy
- Biogas: Created by the decomposition of organic matter in the absence of oxygen, a process known as anaerobic digestion. Common sources include animal manure, food scraps, and wastewater sludge.
Once collected, this gas, rich in methane, can be burned directly for heat or electricity or even refined and used as a natural gas substitute.
- Biofuel: Liquid fuels derived from biomass. The two most common types are ethanol, often made from corn or sugarcane, and biodiesel, derived from vegetable oils or animal fats.
These fuels can be blended with traditional gasoline and diesel or used on their own in certain engines.
- Biomass: Organic materials, such as wood chips, crop residues, or even algae, which can be burned or biologically processed to produce electricity, heat, or fuel. It’s a versatile source that can be utilized in many different ways, depending on the material and the desired output.
Environmental Considerations and Scalability
Bioenergy holds promise for several reasons:
- Carbon Neutral: The carbon dioxide released when bioenergy is produced and used, is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed by plants as they grow, making the process potentially carbon neutral.
However, it’s essential to ensure that biomass is sourced sustainably without leading to deforestation or ecosystem degradation.
- Waste Reduction: By turning waste products, like food scraps or agricultural residues, into energy, we not only produce power but also tackle the issue of waste management.
- Local Energy Production: Bioenergy can be produced locally, reducing the need for extended supply chains and promoting local economies.
However, it’s crucial to understand that bioenergy isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. The viability of different bioenergy sources varies depending on regional factors like climate, soil type, and available resources.
The Road Ahead for Bioenergy
While bioenergy is already a significant player in the renewable energy sector, continuous research is paving the way for even more efficient and sustainable methods.
Advanced biofuels, produced from non-food crops or algae, promise higher energy outputs with lower environmental impacts.
Technologies that combine biomass burning with carbon capture and storage could even result in negative carbon emissions, actively reducing the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere.
Conclusion
Green energy is the future, and the best green energy alternatives include Solar Power, Geothermal energy, wind power and bioorganics.
Personally, I have a soft spot for these sources of energy, probably stemming from the fact that I have used them and have found them to be amazing and reliable in all ways.
Thanks for reading the article; you can also check out our website for more related articles.
Related posts:
- 389 Adjectives Starting with Z (Positive Words and Others) - January 12, 2024
- 389 Adjectives Starting with Y (Positive words and Others) - January 11, 2024
- 389 Adjectives Starting with X (Positive words and Others) - January 10, 2024