Some of the best green transportation solutions include walking, biking, electric cars and carpooling.
In today’s rapidly evolving world, there’s an increasing need for sustainability in every corner of our lives, and transportation is no exception.
As our planet grapples with environmental challenges, the spotlight is firmly on the immense carbon footprint left behind by conventional means of transportation.
However, as the urgency for change grows, so too does the demand for green transportation solutions.
Transportation is responsible for nearly a quarter of global carbon dioxide emissions from fuel combustion. This alarming statistic underscores the importance of seeking more sustainable, eco-friendly methods of commuting.
Beyond the statistics and the urgency to protect our planet, there are also numerous personal benefits that come with adopting green transportation solutions—ranging from better health to potential cost savings.
Our focus in this guide is to delve into green transportation solutions that not only benefit the environment but also cater to our modern-day needs. By understanding the significance, benefits, and options available, we can each take steps towards a more sustainable future—one commute at a time.
The Rise of Green Transportation Solutions

Over the past few decades, the way we view transportation has drastically evolved. Traditional modes of transport, fueled predominantly by gasoline and diesel, have been a substantial contributor to environmental concerns, notably climate change.
As the realities of global warming, air pollution, and diminishing fossil fuels became more apparent, the call for more sustainable, green transportation solutions grew louder.
A Brief History of Transportation’s Environmental Impact
From the Industrial Revolution to the late 20th century, transportation advancements prioritized speed, efficiency, and scale. Railroads crisscrossed continents, cars became household essentials, and international flights bridged distant lands.
While these developments transformed global societies, they also escalated carbon emissions and pollutants. For example, the transportation sector accounts for about 14% of global greenhouse gas emissions, with road vehicles being the primary contributors.
Recent Trends and Statistics on Eco-Friendly Commuting
As the 21st century dawned, so did a heightened awareness of our ecological footprint. City planners, policymakers, and everyday commuters began looking for ways to reduce the environmental toll of their daily travels. Some notable trends and stats include:
1. Global EV Sales Surge
Electric vehicle sales witnessed a sharp rise, with estimates suggesting they could account for up to 58% of new car sales by 2040.
2. Public Transit Revival
Cities worldwide have invested in greening their public transit systems. From electric buses in Shenzhen, China, to expanding metro networks in European cities, public transit is becoming a cleaner option.
3. Bike-Friendly Urban Planning
Urban areas, including cities like Copenhagen and Amsterdam, have seen an exponential increase in daily cyclists, thanks to dedicated bike lanes, bike-sharing programs, and public campaigns.
4. Remote Work and Digital Commutes
With advances in digital technology and in response to global events like the COVID-19 pandemic, telecommuting has reduced the need for daily physical commutes for many, decreasing transportation-related emissions.
Different Types of Green Transportation Solutions
1. Walking and Biking
Walking and biking are foundational modes of transport that have existed for millennia. They remain the most energy-efficient and environmentally benign means of moving from one place to another.
Walking requires no infrastructure, fuel, or special equipment besides perhaps a pair of comfortable shoes. In urban settings, promoting walking can mean pedestrianizing certain areas or ensuring safe sidewalks.
Biking, on the other hand, has seen a renaissance in urban planning. Many cities worldwide are expanding their cycling infrastructure by adding dedicated bike lanes, bike-sharing programs, and storage facilities.
Bicycles offer a swift means of transport in congested areas and serve as an excellent solution for the ‘last mile’ problem in urban transit.
The environmental benefits are obvious: zero emissions and no resource consumption (besides human calories). Moreover, the health benefits are significant, as these modes promote cardiovascular health, muscle building, and mental well-being due to increased endorphin production.
2. Public Transport
Public Transport, including buses, trams, subways, and commuter trains, is a staple of urban mobility and one of the best green transportation solutions.
Its capacity to move large numbers of people efficiently reduces the need for individual car journeys, resulting in fewer emissions.
Cities are actively improving their public transport systems. Many buses are transitioning from diesel to electric or hybrid models.
Trams and trains are being optimized for energy consumption, and many metro systems worldwide are moving towards 100% renewable energy sources.
Beyond environmental benefits, public transportation offers social benefits: it reduces traffic congestion, decreases road accidents, and often provides a more affordable travel option for many people.
For cities, investing in efficient public transit can lead to less spending on road infrastructure and maintenance in the long run.
3. Carpooling and Ridesharing
Carpooling and Ridesharing involve sharing a single vehicle for multiple passengers. This reduces the number of cars on the road and promotes a communal approach to transportation.
Modern technology has given a significant boost to this age-old idea. Platforms like UberPool, Lyft Shared, and local carpooling apps connect riders traveling in the same direction. They optimize routes to ensure minimal detours.
The environmental benefits are significant. Fewer cars result in reduced emissions and less wear and tear on roads.
Additionally, carpooling can lead to significant cost savings for individuals when you consider fuel, tolls, and parking fees.
This makes it one of my favorite green transportation solutions, especially when you want to do road trips with some company.
4. Electric Vehicles (EVs)
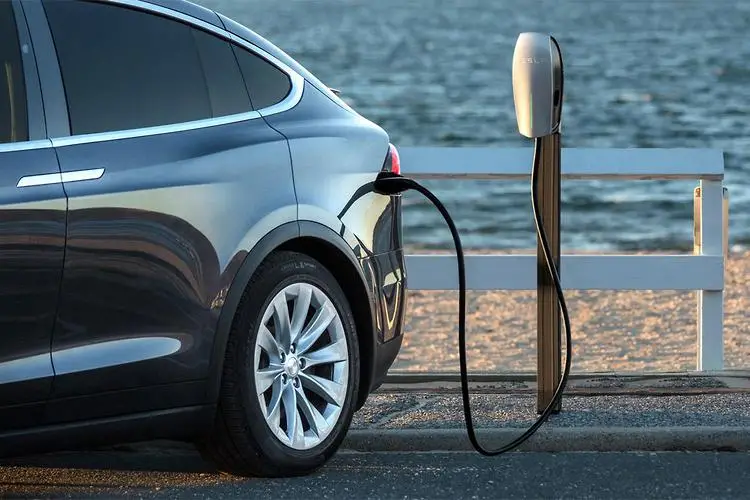
Electric Vehicles (EVs) have emerged as a frontrunner in the race towards sustainable transportation. They operate on electricity, producing zero tailpipe emissions.
With advancements in battery technology, the range and performance of EVs have increased drastically. Charging infrastructure is expanding, with fast-charging stations now commonplace in many urban areas and along major highways.
It’s essential to view EVs in the broader context of the energy grid. Their environmental impact is most beneficial when the electricity is sourced from renewable resources.
With the global shift towards green energy, EVs present a future where transportation doesn’t contribute to carbon emissions.
5. Hybrid Vehicles
Hybrid Vehicles are one of the amazing green transportations solutions that combine traditional combustion engines with electric propulsion.
Hybrids offer a compromise for those not ready to switch entirely to electric. They use an electric motor for low-speed driving, typically in city conditions, and switch to gasoline for higher speeds or when the battery is low.
This combination results in better fuel efficiency and fewer emissions compared to conventional vehicles.
As battery technology and infrastructure for EVs improve, hybrids will likely be a stepping stone for many users before transitioning to full electric.
6. Alternative Fuel Vehicles
Alternative Fuel Vehicles are those that run on something other than gasoline or diesel. These can include biofuels like ethanol or biodiesel, compressed natural gas (CNG), or hydrogen fuel cells.
Each alternative fuel source has its benefits and challenges. For instance, while biofuels are renewable, their production can have significant environmental impacts depending on farming practices.
Hydrogen fuel cells produce only water as a by-product, but producing hydrogen efficiently and sustainably remains a challenge.
These alternatives offer pathways to reduce dependence on oil and diversify the energy sources used in transportation.
Challenges to Adopting Green Transportation Solutions
1. Infrastructure Needs
- Inadequate Charging Stations: Electric Vehicles (EVs) are only as good as the infrastructure supporting them. One of the primary concerns for potential EV owners is the scarcity or uneven distribution of charging stations, often termed “range anxiety.” In many regions, especially in rural areas, charging facilities are sparse, making long trips challenging.
- Public Transport Limitations: Cities and urban areas worldwide are grappling with outdated public transportation systems that aren’t equipped to handle modern green technologies. Implementing cleaner and more efficient vehicles requires not just the vehicles themselves but often a revamp of the existing transport network.
- Road Safety for Non-Motorized Transport: While walking and biking are among the eco-friendliest modes of transport, in many cities, there’s a lack of proper lanes, pathways, and safety measures for pedestrians and cyclists. This absence can deter people from considering these options despite their benefits.
2. Initial Cost Barriers
- High Upfront Costs: Despite the total cost of ownership of EVs and hybrid vehicles often being lower than conventional vehicles, the initial investment can be substantially higher. This price tag can be a deterrent for many potential buyers, even if they are aware of the long-term savings.
- Lack of Financial Incentives: In areas where governments or local bodies do not offer tax breaks, subsidies, or rebates for green vehicles, the adoption rate tends to be slower. Financial incentives can significantly boost the attractiveness of sustainable transport options.
3. Behavioral Change and Societal Adjustments
- Perception and Awareness: A significant section of society remains unaware of the full benefits of green transportation. Moreover, some people hold misconceptions about the performance, reliability, and convenience of eco-friendly vehicles, especially EVs.
- Cultural Norms and Car Ownership: In many societies, owning a car, particularly a luxury or high-performance vehicle, is seen as a status symbol. This perception can be a barrier to adopting shared mobility solutions or even opting for smaller, eco-friendly vehicles.
- Resistance to Change: Humans, by nature, can be resistant to change. For many, the idea of shifting from a tried-and-tested transportation method to a new, unfamiliar one can be daunting. Overcoming this mindset requires a combination of education, incentives, and exposure to the benefits of green solutions.
4. Technological Challenges
- Battery Technology: While strides have been made in battery technology for EVs, there remain concerns about their longevity, charging speed, and the environmental implications of their disposal.
- Alternative Fuels: Biofuels, hydrogen, and other alternatives to conventional fuels are in varying developmental stages. These options face challenges in production scalability, storage, distribution, and establishing a solid market presence.
Tips For Making the Shift to Eco-Friendly Commuting
Making the transition to green transportation solutions is not just a societal imperative but also an individual commitment towards a healthier planet.
It’s about making conscious choices that not only benefit the environment but can also enhance your well-being and potentially reduce expenses.
Below, we delve into a range of actionable tips that you, as an individual or organization, can adopt to contribute to the wave of eco-friendly commuting.
Individual-Level Changes
- Assess Your Current Commuting Habits: Start by understanding your existing transportation patterns. How far is your daily commute? What mode of transport do you usually use? This assessment can help identify the most significant areas for improvement.
- Embrace Active Transportation: Whenever possible, choose walking or biking over motorized transport. Not only do these options produce zero emissions, but they also offer considerable health benefits. Investing in a good-quality bike, comfortable walking shoes, or even a pedestrian-friendly route can make this shift more enjoyable and sustainable in the long run.
- Opt for Public Transportation: Buses, trains, and trams are significantly more efficient in terms of emissions per passenger compared to single-occupancy vehicles. If public transportation options are available and practical for your commute, make it a habit to use them. Not only will you be reducing your carbon footprint, but you’ll also save on fuel costs and wear and tear on your personal vehicle.
- Carpooling and Ridesharing: Sharing a ride can significantly cut down on individual carbon emissions. Apps and community boards can connect you with others on similar routes. Additionally, many cities offer High-Occupancy Vehicle (HOV) lanes that can make carpooling an even more efficient option.
- Telecommuting: The rise of remote work has shown that not every job requires a daily commute. If your profession allows, negotiate with your employer for the option to work from home part or all of the time. This not only saves on commuting emissions but can also increase your productivity and work-life balance.
Organizational-Level Initiatives
- Implement a Green Commuting Policy: Organizations can lead the way by adopting policies that encourage eco-friendly commuting. This might include flexible hours to allow for off-peak travel, telecommuting options, or incentives for employees who carpool or use public transportation.
- Provide On-Site Amenities: Companies can support active commuting by providing amenities such as bike racks, showers, and changing facilities. These small additions can make a big difference in employees’ willingness to bike or walk to work.
- Subsidize Public Transport: Offering subsidized or free public transportation passes is an excellent incentive for employees to leave their cars at home. This can be a part of the benefits package and can also be tax-deductible in some regions.
- Establish a Corporate Carpool Program: Create an internal system that helps employees connect with others who live nearby and have similar schedules. Providing priority parking for carpool vehicles can be an added incentive.
Community and Governmental Actions
- Advocacy for Better Infrastructure: Advocating for improved cycling paths, pedestrian walkways, and efficient public transportation can make eco-friendly commuting more accessible and safer for everyone.
- Support for Local Initiatives: Participate in or support local programs that promote green transportation. These can include community bike-share programs, car-free day events, or campaigns to improve public transit.
- Incentivising Green Vehicles: Governments can offer incentives such as tax breaks, rebates, or grants for individuals and businesses that purchase electric or hybrid vehicles.
- Zoning for Accessibility: Advocating for zoning policies that promote mixed-use developments can ensure that residential areas are close to workplaces, shopping, and other amenities, reducing the need for long commutes.
The Future of Green Transportation
Let’s dive into what the coming years might hold for eco-friendly commuters.
Autonomous Electric Shuttles and Buses
One of the most anticipated advancements in the realm of sustainable transportation is the fusion of autonomous technology with electric vehicles.
The introduction of driverless electric shuttles and buses offers a dual benefit: not only can they operate with zero emissions, but they can also optimize routes and reduce traffic congestion, further minimizing their environmental footprint.
Pilot programs in cities like Las Vegas and Stockholm are already testing these vehicles, aiming to integrate them into public transportation systems in the coming decade.
Urban Air Mobility: Air Taxis and Drones
The dream of flying cars might soon be a reality, albeit in a different form than many imagined. Urban Air Mobility (UAM) is an emerging sector focusing on using airspace to alleviate urban transportation challenges.
Electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) vehicles, commonly referred to as “air taxis,” promise quick intra-city travel with minimal emissions.
Companies like Uber Elevate and Joby Aviation are leading the charge, projecting that short air commutes will become an integral part of our transportation matrix within the next 15 years.
Magnetic Levitation (Maglev) Trains
While Japan and Germany have been experimenting with maglev technology for decades, we are on the cusp of seeing wider adoption globally.
These trains use magnets for lift and propulsion, allowing them to achieve incredible speeds with a fraction of the energy consumption of traditional trains.
The elimination of friction not only makes them more efficient but also reduces wear and tear, translating to lower maintenance costs and longer lifespans.
Expansion of EV Charging Infrastructure
As electric vehicle adoption soars, the need for expansive and efficient charging infrastructure becomes paramount. We are likely to witness an explosion in the number of charging stations, equipped with faster charging capabilities.
Additionally, innovations such as wireless charging lanes and solar-powered charging stations could redefine how EVs interact with the grid.
Sustainable Fuel Breakthroughs
While electric powertrains are gaining traction, there’s active research in developing sustainable fuels that can replace or complement traditional fossil fuels.
From algae-based biofuels to synthetic fuels created using renewable energy, the quest for a green fuel solution could reshape sectors resistant to electrification, such as aviation and heavy-duty transportation.
Integration of Green Transportation with Smart Cities
The cities of the future are expected to be data-driven, connected, and sustainable. Integration of green transportation solutions into the smart city ecosystem can lead to dynamic traffic management, predictive maintenance of transport assets, and real-time route optimization, all aimed at reducing emissions and enhancing the commuter experience.
Policy and Regulation Shifts
As governments recognise the environmental and economic benefits of green transportation, there’s an increasing push to incentivize sustainable practices.
From stricter emissions standards to subsidies for EV buyers, policy instruments will play a crucial role in determining the pace and direction of transportation’s green revolution.
Conclusion
And that’s the end of the article. We explored in detail what green transportation really entails, we looked at some of the best green transportation alternatives, as well as their challenges.
I am very optimistic that in the next 10 years, the world will come to accept green transportation as the new permanent thing.
Thanks for reading; check out our website for more related articles.
Related posts:
- 389 Adjectives Starting with Z (Positive Words and Others) - January 12, 2024
- 389 Adjectives Starting with Y (Positive words and Others) - January 11, 2024
- 389 Adjectives Starting with X (Positive words and Others) - January 10, 2024