Yes, fossil fuels are the main cause of climate change.
What Are Fossil Fuels?
Fossil fuels, the cornerstone of modern energy consumption, are derived from the remnants of ancient organisms. Coal, formed from decomposed plant matter over millions of years, has been a historical energy bedrock.
Oil, a liquid treasure extracted from marine microorganisms, and natural gas, often found in association with oil deposits, complete the triumvirate. These hydrocarbons, laden with carbon and hydrogen, possess an unparalleled energy density, making them efficient fuels.
As society expanded during the Industrial Revolution, the demand for fossil fuels skyrocketed. Coal became the backbone of early industrial processes, powering steam engines and factories.
The advent of the internal combustion engine in the 19th century saw oil take center stage, propelling the transportation revolution. Natural gas, cleaner and more versatile, found favor in heating homes and generating electricity.
However, the prolific use of fossil fuels comes at a hefty environmental cost. The combustion of these hydrocarbons releases copious amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere, contributing significantly to the menacing specter of climate change.
Understanding the historical significance and environmental implications of fossil fuels and climate change is crucial as we navigate the complex terrain of energy transition.
Examples of Fossil Fuels
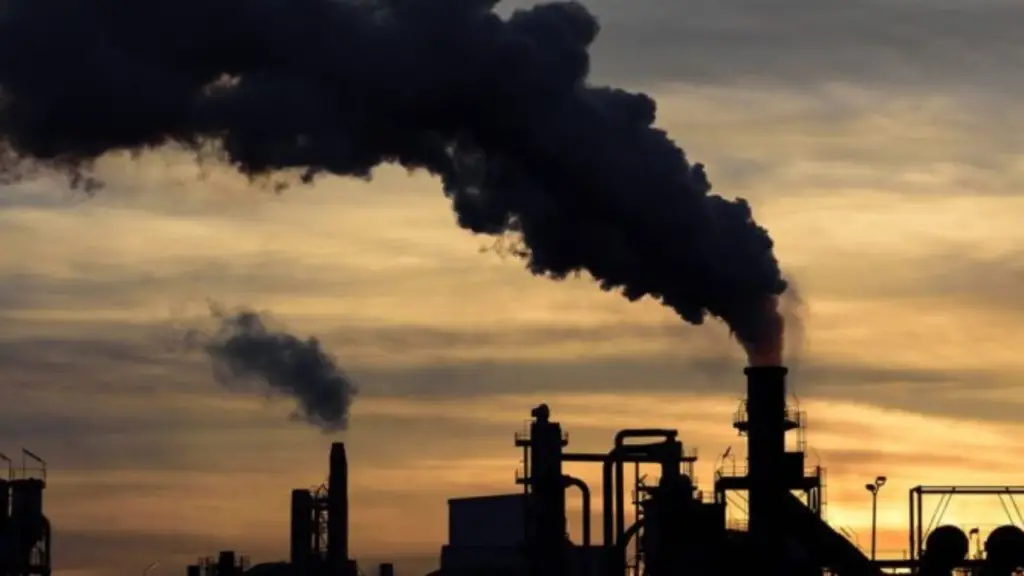

Delving into specific examples of fossil fuels unveils the breadth of their usage and impact on various aspects of modern life. Each type—coal, oil, and natural gas—has distinct characteristics, applications, and environmental implications that contribute to the intricate narrative of fossil fuels.
1. Coal
Coal, a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, has been a historical source of stability and security in energy generation.
It is an age-old stalwart in the records of energy production and has played a pivotal role in shaping the trajectory of industrialization.
Composed of ancient plant matter compressed over geological periods, coal’s energy density made it the backbone of the Industrial Revolution.
Mined from vast reserves worldwide, coal has fueled electricity generation, industrial processes, and residential heating. It powered steam engines, fueled factories, and illuminated cities, ushering in a new era of progress.
However, the environmental ramifications of coal combustion cast a long shadow. Burning coal releases copious amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other pollutants, contributing significantly to air pollution and climate change.
Sulfur dioxide emissions, a byproduct of coal combustion, lead to acid rain, further compromising air and water quality. The mining process can result in habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water contamination, leaving ecosystems in disarray.
Despite its historical significance, the environmental toll of coal has prompted a global shift towards cleaner energy alternatives.
The imperative to phase out coal in favor of sustainable options is not merely a matter of progress but a necessity for mitigating climate change and preserving the delicate balance of our ecosystems.
2. Oil
Crude oil, often referred to as black gold and extracted from beneath the Earth’s surface, is a versatile fossil fuel with extensive applications. Refined into petroleum, it powers the transportation sector, fueling cars, planes, and ships.
Due to its refinement into petroleum, it has birthed multiple products, from gasoline powering our vehicles to petrochemicals forming the basis of plastics and pharmaceuticals.
While indispensable to modern life, the widespread use of oil intensifies environmental concerns due to its role in climate change and ecological disruptions.
The environmental implications of oil usage are profound. The combustion of petroleum products, especially in internal combustion engines, releases not only CO2 but also other pollutants harmful to air quality.
Oil spills from extraction or transportation pose catastrophic threats to marine ecosystems, impacting biodiversity and devastating coastlines.
The quest for oil has also driven geopolitical tensions, leading to conflicts and environmental degradation in sensitive regions.
The urgency to transition away from oil dependency is underscored by the imperative to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, enhance energy security, and mitigate the ecological fallout associated with oil exploration and consumption.
3. Natural Gas
Natural gas, primarily composed of methane, is a cleaner-burning fossil fuel than coal and oil.
Widely used for heating homes, generating electricity, and as a feedstock in industrial processes, natural gas has become a cornerstone of energy transition discussions.
While natural gas combustion emits fewer pollutants and CO2 than coal and oil, it is not without environmental challenges. Methane, a potent greenhouse gas, can escape during extraction and transportation, contributing to global warming.
Hydraulic fracturing or fracking, a standard method of natural gas extraction, raises concerns about water contamination and habitat disruption. Its extraction and transportation also pose environmental challenges.
Understanding these examples sheds light on the pervasive influence of fossil fuels in shaping our energy landscape. While indispensable to the development of modern societies, their environmental drawbacks necessitate a concerted effort to transition toward sustainable alternatives.
This transition, driven by innovation and collective commitment, is crucial to mitigating the environmental impact of fossil fuel usage.
Despite these challenges, natural gas remains crucial in the ongoing energy transition. Its role in balancing energy demands while minimizing carbon emissions highlights the complexities of our energy choices.
Striking a balance between harnessing natural gas’s benefits and addressing its environmental impact is essential for navigating the path toward a more sustainable and resilient energy future.
Disadvantages of Fossil Fuels
1. Air Pollution
Fossil fuel combustion is a primary contributor to air pollution. Emissions of pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter lead to respiratory issues and degrade air quality.
The combustion of coal, in particular, releases not only carbon dioxide but also pollutants like sulfur dioxide, contributing to acid rain and other environmental issues.
While fossil fuels significantly contribute to air pollution, several other sources compound environmental challenges, forming a complex web of pollutants that impact air quality and contribute to climate change.
- Industrial Emissions
Industries emit many pollutants, including particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, and volatile organic compounds. Manufacturing processes, power generation, and chemical production contribute significantly to air pollution. Implementing cleaner technologies and stringent regulations are essential for mitigating industrial emissions.
- Agricultural Practices
Agriculture is a notable source of air pollution, primarily through ammonia emissions from fertilizers and methane released by livestock.
Ammonia contributes to particulate matter formation and can harm respiratory health, while methane is a potent greenhouse gas. Reducing emissions relies on the adoption of sustainable farming practices and the implementation of innovative approaches.
- Vehicle Exhaust
Combustion engines in vehicles emit pollutants such as nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and particulate matter. The widespread use of automobiles contributes to urban air pollution and poses health risks.
Transitioning to electric vehicles, improving public transportation, and implementing stricter emission standards are critical strategies for addressing this source of pollution.
- Waste Management
Improper waste disposal and treatment contribute to air pollution by releasing methane from landfills. Open burning of waste exacerbates the problem by emitting harmful pollutants.
Adopting sustainable waste management practices, including recycling and controlled waste-to-energy processes, is vital for reducing these emissions.
- Deforestation and Biomass Burning
Deforestation and biomass burning, such as forests and agricultural residues, release significant amounts of carbon dioxide and particulate matter into the air.
Preserving forests, implementing sustainable land-use practices, and promoting alternatives to biomass burning are essential for mitigating these emissions.
2. Climate Change
The most profound disadvantage is the link between fossil fuels and climate change. The release of greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide, enhances the greenhouse effect, leading to global warming.
The resulting climatic changes, from extreme weather events to rising sea levels, threaten ecosystems, communities, and biodiversity.
3. Environmental Degradation
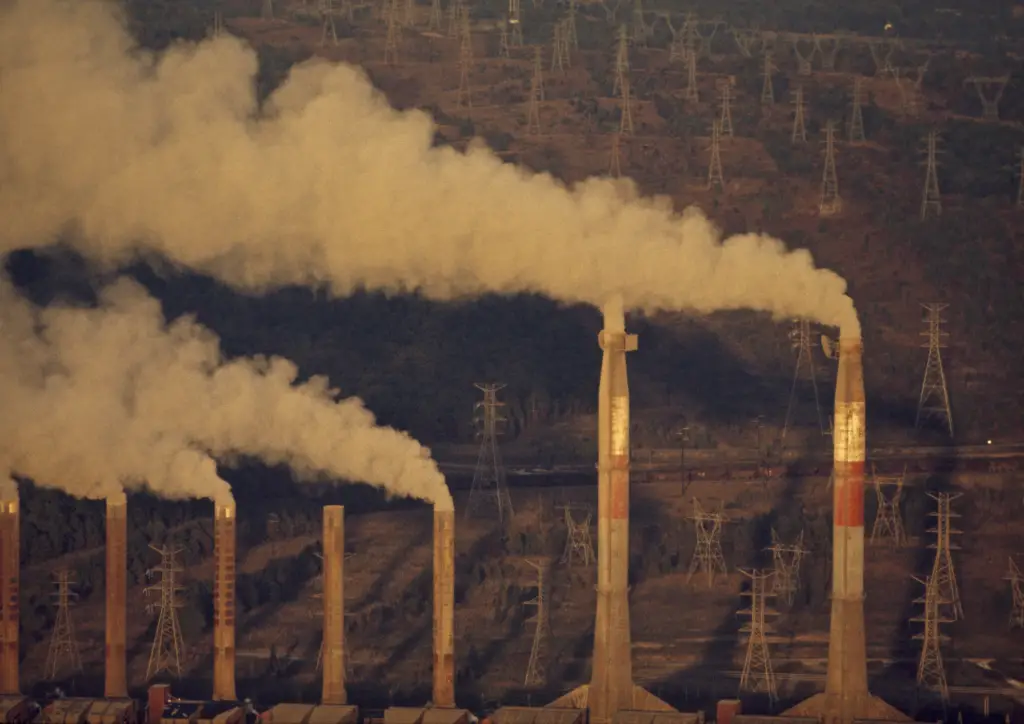

The extraction of fossil fuels often involves habitat destruction and disruption of ecosystems. Deforestation, soil degradation, and disruption of water sources are expected consequences.
Oil spills from extraction and transportation activities can have catastrophic effects on aquatic ecosystems and wildlife.
4. Resource Depletion
Fossil fuels are finite resources, and their extraction often involves exploiting pristine environments. As easily accessible reserves diminish, the quest for more challenging sources leads to more significant environmental risks, such as deep-sea drilling or extraction from ecologically sensitive areas.
5. Health Impact
Beyond environmental concerns, the combustion of fossil fuels contributes to health issues. Air pollutants emitted during combustion, such as delicate particulate matter and ozone, are linked to respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and other health issues.
Growing up in an area where there was gas flaring, I observed many children and adults with long-lasting respiratory illnesses.
6. Energy Security Concerns
Reliance on fossil fuels poses energy security challenges. Nations heavily dependent on fossil fuel imports are susceptible to geopolitical tensions and price fluctuations, making their energy supply vulnerable to external factors.
Link Between Fossil Fuels and Climate Change
The intricate link between fossil fuels and climate change lies in the emissions produced when these fuels are burned for energy. Fossil fuel combustion releases a cocktail of greenhouse gases, with carbon dioxide (CO2) taking center stage.
As these gases accumulate in the atmosphere, they form a proverbial blanket, trapping heat and causing a gradual rise in global temperatures—a phenomenon known as the greenhouse effect.
This warming of the planet leads to a cascade of environmental consequences. Glacial and polar ice melt, causing sea levels to rise and threaten low-lying coastal regions.
Erratic weather patterns intensified storms, and altered precipitation cycles became more prevalent, impacting ecosystems and human communities. The interconnected web of life on Earth is disrupted as species struggle to adapt to fossil fuels and climate change.
Recognizing the link between fossil fuels and climate change is vital. The scientific consensus is clear: burning fossil fuels is a primary driver of global warming.
Acknowledging this connection is the first step toward implementing sustainable practices and transitioning to cleaner, renewable energy sources that mitigate the adverse impacts on our planet.
Impact of Fossil Fuels and Climate Change on Our Planet
The impact of fossil fuels and climate change is visible all across the globe, leaving an indelible mark on the delicate balance of our planet.
As the combustion of fossil fuels continues unabated, the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere intensifies, increasing the greenhouse effect and leading to a series of far-reaching consequences.
One of the most pronounced impact of fossil fuels and climate change is the rise in global temperatures, contributing to phenomena like heat waves, droughts, and changing precipitation patterns.
During the last three years, I’ve observed a shift in the weather pattern. It’s warmer than usual, even during the last months of the year.
Melting ice caps and glaciers, directly resulting from this warming trend, contribute to rising sea levels, imperiling coastal communities and ecosystems. The intricate dance of biodiversity is disrupted as species struggle to adapt or face the risk of extinction.
Moreover, the repercussions extend beyond climatic shifts. Ocean acidification, caused by absorbing excess CO2 from seawater, threatens marine life, particularly coral reefs, and shell-forming organisms.
Deforestation, often linked to resource extraction for fossil fuels, further amplifies environmental degradation, eroding ecosystems crucial for biodiversity and carbon sequestration.
The urgency to address the impact of fossil fuels and climate change is paramount. Sustainable alternatives and mitigation strategies must be embraced to safeguard the health of our planet.
By understanding the broader consequences, we can collectively strive for a future where the adverse effects of fossil fuel dependency are mitigated and the delicate balance of our global ecosystem is preserved.
Can We Keep Burning Fossil Fuels?
Whether we can sustainably continue burning fossil fuels is a critical crossroads in our journey toward a sustainable future.
The undeniable reality is that the current trajectory, marked by relentless fossil fuel consumption, is incompatible with long-term environmental health.
The imperative for change is clear, grounded in the understanding that continued reliance on these non-renewable resources poses an existential threat to our planet.
The crux lies in the inherent link between fossil fuels and climate change. The release of greenhouse gases, especially carbon dioxide, during combustion, contributes significantly to global warming.
The consequences of unchecked climate change are far-reaching, affecting ecosystems, weather patterns, and human societies.
While the imperative to transition away from fossil fuels is clear, the journey toward a sustainable energy future is complex. Technological advancements in renewable energy offer promising alternatives, yet the transition requires concerted efforts on multiple fronts.
Investments in research and development, policy interventions, and societal shifts toward more sustainable practices are essential components of a comprehensive strategy.
Phasing out fossil fuels requires balancing economic considerations, social equity, and environmental responsibility. Government initiatives, corporate commitments, and individual choices collectively shape the direction of our energy future.
A paradigm shift is imperative in contemplating whether we can keep burning fossil fuels. It requires acknowledging the situation’s urgency, embracing innovation, and fostering a collective commitment to sustainable practices.
The future viability of our planet rests on our ability to navigate this transition and build a world where energy needs are met without compromising the delicate balance of our environment.
Role of Fossil Fuel Companies in The Future
Fossil fuel companies’ role in shaping our planet’s future is essential, as they stand at the center of energy production and environmental impact.
These companies, often influential global entities, have the agency to steer the path toward sustainability or bring about environmental degradation.
Examining their role requires analyzing their current practices, commitments to change, and potential contributions to a greener future. Fossil fuel companies have historically been central to meeting the world’s energy demands.
However, this very contribution has been a significant driver of climate change. The extraction, processing, and combustion of fossil fuels are linked to greenhouse gas emissions, amplifying the urgency for these companies to transition to more sustainable practices.
The future trajectory of fossil fuel companies depends on their responsiveness to the increasing climate crisis. Many recognize the imperative for change and commit to reducing their carbon footprint.
Investments in renewable energy technologies, carbon capture and storage initiatives, and transitioning to cleaner production methods are becoming critical components of corporate strategies.
Governments and consumers also play a role in influencing the behavior of fossil fuel companies. Regulatory frameworks that encourage sustainable practices and penalize environmental negligence can catalyze change.
Simultaneously, consumer choices can shape corporate strategies driven by awareness and demand for environmentally responsible products and services.
As we navigate the energy transition, fossil fuel companies can play a transformative role in controlling climate change. The future hinges on their ability to adapt, innovate, and align their operations with sustainable practices.
Whether they become catalysts for positive change or obstacles to progress will significantly influence the collective efforts to build a more sustainable and resilient future.
Conclusion
Fossil fuels, once heralded as the driving force behind industrialization and progress, now stand at the forefront of an environmental crossroads.
While their drawbacks cast a looming shadow, these energy sources have likewise shaped societies and economies, from the historical significance of coal to the versatile applications of oil and natural gas.
The narrative of fossil fuels and climate change is not one of certainty but of choice. The choices we make today will resonate through generations, determining the health of our planet.
Embracing cleaner alternatives, advocating for policy changes, and fostering environmental stewardship are the pillars of a sustainable future.
Related posts:
- 389 Adjectives Starting with Z (Positive Words and Others) - January 12, 2024
- 389 Adjectives Starting with Y (Positive words and Others) - January 11, 2024
- 389 Adjectives Starting with X (Positive words and Others) - January 10, 2024