Reviewed by Ogbo Godfrey
Dietitians recommend a sustainable meat consumption level of no more than 455g per week or a daily maximum of 14g to promote healthy eating habits and environmental sustainability.
The meat debate has been ongoing for a long period. The two groups, the meat lovers and the vegans have gone head to head in a battle involving facts, statistics, and, unsurprisingly, death. There’s no clear winner, and there will be no clear loser anytime soon. However, which side should we be on?
Sustainable meat consumption is an essential topic in our world today. With the population increase and the rapid inflation in food prices, it is essential to know how much meat is sustainable for consumption.
There are pros and cons to eating meat. For every nutrient we get, some argue there’s an effect waiting around the corner. So what exactly should be the sustainable meat consumption level?
In this article, we’ll highlight the sustainable meat consumption and give guidelines for intelligent consumer decisions.
What exactly is meat?
Meat is the flesh of animals that can be eaten raw or cooked.
It refers to the fat and muscles of animals. It also includes the edible organs such as the heart, intestines, kidney, brain, etc. These are collectively known as offal.
Types of Meat
1. Red meat

Meat contains myoglobin, a protein found only in mammals and includes a high iron level. Red meat has a higher myoglobin level than white meat.
Examples of red meat are:
- goat
- veal from calves
- lamb
- pork, from hogs and pigs
- venison from deer
- beef from cattle
2. White meat

White meat usually refers to the meat from birds. The meat has a light colour, raw or cooked.
3. Processed meat
Processed meat is a red and white meat treated to aid preservation or improve its taste, colour or smell.
Processed meat includes bacon, sausage, beef, bologna, hot dog, etc.
What are the nutrients in meat?
To achieve an optimal sustainable meat consumption, it is important to know the nutrients in meat. Below are the key nutrients.
1. Vitamins
Meat contains Vitamin A (retinol), Vitamin B12, Vitamin D, and other vitamins. Vitamin D has two forms; ergocalciferol (D2) and cholecalciferol (D3).
D2 is found in plants and D3 is found in animals. Although both D2 and D3 are essential, studies indicate the ease of absorbance of D3 than D2.
2. Iron
Iron has two types; heme and non-heme iron. Heme iron is found in red meat and non-heme iron is found in plants. Unsurprisingly, heme iron is absorbed more easily than non-heme iron
3. Choline
Choline is an essential nutrient that is found in meat. It is very important for brain health and the formation of the cell membrane. It also aids in liver and muscle stimulation.
Other than these three, important nutrients are majorly found in meat. Some of these are; Carnitine, Carnosine, Taurine, Creatinine, etc.
Recommended sustainable meat consumption
In a recommended sustainable meat consumption, moderation is always the limit in all things, especially food. Meat contains 25-30% protein by weight after cooking. Cooked 100g serving of chicken breast has roughly a protein value of 31g, while the exact size of beef contains about 27g.
Dietitians recommended servings of cooked red meat of a maximum of 455g weekly. This value is recommended to ensure that iron and zinc levels are stable in the body. A small portion of meat to be eaten daily would weigh 65g if cooked and 100g if raw.
The EAT-Lancet Commission recommends changing diet towards plant-based foods and limiting meat consumption to at least 14g per day. This encourages an optimal sustainable meat consumption.
Most of us already eat the recommended daily amount of meat, and some even exceed it. Meat consumption is recorded to be higher among teenagers and men aged 14-50.
As shown in the statistics, women often have a lower meat consumption level, and this is not meant to be because women have greater iron recommendations than men.
What are the factors that influence sustainable meat consumption?
Let’s dive into key factors that influence sustainable meat consumption
1. Consumption frequency
Consuming meat frequently is bad for the health and the environment. It’s essential to gain nutrients, but minimizing the number of times meat is consumed will have a positive impact on the body.
Rather than taking meat daily, reduce the consumption to 2 or 3 times weekly.
2. Portion size
Reducing the size of meat consumed daily will help reduce waste. It also balances the diet, as it doesn’t make sense to reduce meat consumption to a few days per week while consuming sizes that you would typically eat in a week.
3. Meat type
The type of meat consumed is also important. There are several types of nutrients found in different sources of meat. Switching between various types is good as they have different nutrient compositions.
4. Health conditions
People with heart issues such as coronary heart disease or other health conditions like hypertension, high cholesterol levels, and high blood pressure should reduce or eliminate red and processed meat from their diet.
Food plan ideas for sustainable meat consumption
1. Add lean proteins to your diet.
Removing the excess visible fat in the meat before cooking. It reduces the saturated fat amount in the dish. Also, lean meat is a good way to begin a healthy diet.
2. Rotate between animal and plant proteins.
Rotating between different protein meals is a good way to reduce excessive meat consumption. It is also a good tip to achieve sustainable meat consumption.
Draw up a food plan where meat is served once or twice a week, and fish is served once or twice weekly. Other proteins like egg, milk, beans, and nuts can also be added to the food plan.
3. Take some days off for all types of meat.
Vegetables are often side dishes. Be creative and make dishes involving vegetables and fruits. You can add little pieces of meat as a filler, or if you’re committed, you can remove meat from your diet for some days. Doing this, you are on your way to achieving a healthy and sustainable meat consumption.
4. Reduce meat portions
While the importance of sustainable meat consumption cannot be under-emphasized, meat portions should be reduced in the diet to no more significance than your palm.
You can also measure the size of the meat to be eaten and then chop them up into smaller pieces.
Effects of excessive meat consumption
Excessive meat consumption is an enemy to achieving a sustainable meat consumption. There has always been a known link between red meat consumption and many health conditions.
Some of these health conditions are:
1. Cancer
Topping the list is one of the world’s most lethal health conditions. Eating excessive red and processed meat has been linked to colorectal cancer, which has the third-highest mortality rate.
Some research has shown that processed meat increases colon inflammation and may induce or worsen colon problems. The World Health Organization (WHO) announced in 2015 that processed meat was officially listed as a Class 1 carcinogen.
2. Heart conditions
Saturated fats and processed meat have been studied to indicate a rise in cholesterol levels, increasing the chances of having a stroke or a heart attack.
3. Type 2 diabetes
While there have been links to red meat increasing the risk of Type 2 diabetes, no precise analysis has been made.
Alternative meat ideas
1. Offal diet
Offals also offer a high nutrient content. Adding them to your diet can help you slowly wean off meat.
2. Reducing cooking with high heat.
Most people prefer meat overcooked or burnt slightly. This increases the risk of cancer. It is advised to cook meat to a soft texture and avoid charring.
3. Consume more plant-based foods.
Plant-based foods are environmentally better, they’re healthier for the body, and they’re less expensive.
Impact of meat consumption on the environment
The demand for meat has risen globally during the last few decades, and there have been concerns about its environmental impact.
These are a few ways that meat consumption has affected the environment negatively.
1. Water Scarcity
Meat production is a process that uses up as much water as possible. The animals need sufficient amounts of water for cleaning and drinking. In areas with little water, it competes for water with the locals and it leads to water scarcity.
2. Pollution
Animals generate large amounts of waste. Combined with the runoff and manure from farms, it can settle in the ocean and deplete the oxygen in lakes and oceans. This pollutes the ocean, kills aquatic life, and affects the ecosystem.
3. Deforestation
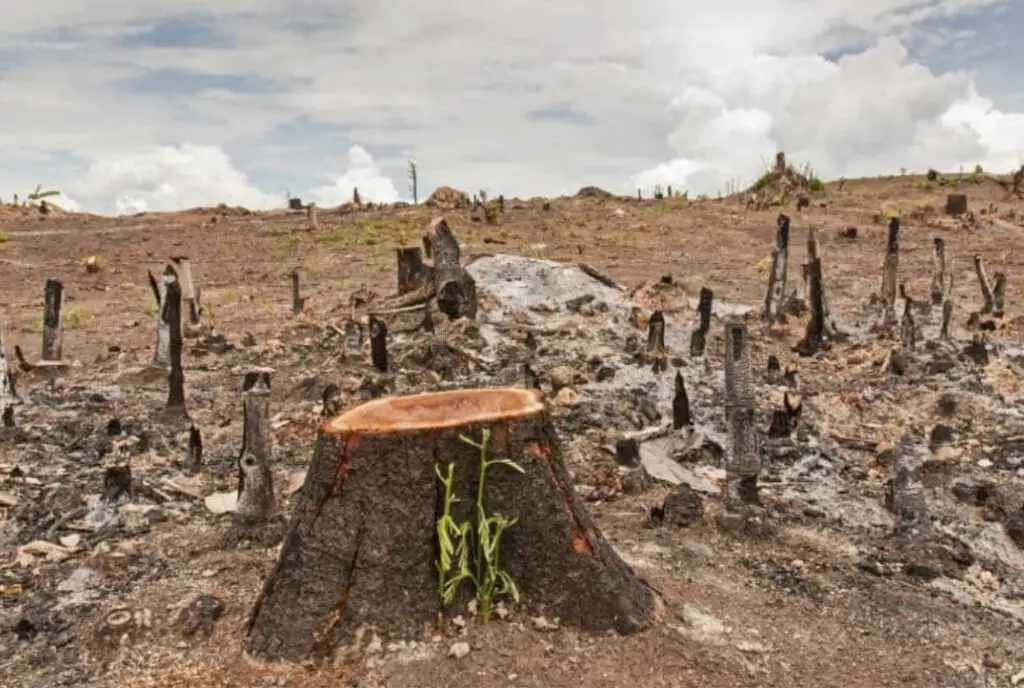

Land is essential for meat production. Livestock graze on large, fertile land areas, leading to deforestation. Trees are cut down to make pastureland in areas such as the Amazon rainforest. Soybeans are then planted and cultivated, which is used to make animal feed.
4. Emissions of gas
Fertilizer production and application, digestion of food in animals, and the improper management of manure release toxic gases such as nitrous oxide into the atmosphere.
According to the United Nations’ Food and Agriculture Organization, an estimated 14.5% of greenhouse gases are contributed by livestock.
Conclusion
Meat contributes to a well-balanced diet, as it is the source of nutrients like iron, vitamins, and proteins. It is important to balance good health and sustainability, and choosing lean meat and minimizing intake is a step forward in ensuring optimal well-being and sustainable meat consumption.
Related posts:
- 389 Adjectives Starting with Z (Positive Words and Others) - January 12, 2024
- 389 Adjectives Starting with Y (Positive words and Others) - January 11, 2024
- 389 Adjectives Starting with X (Positive words and Others) - January 10, 2024