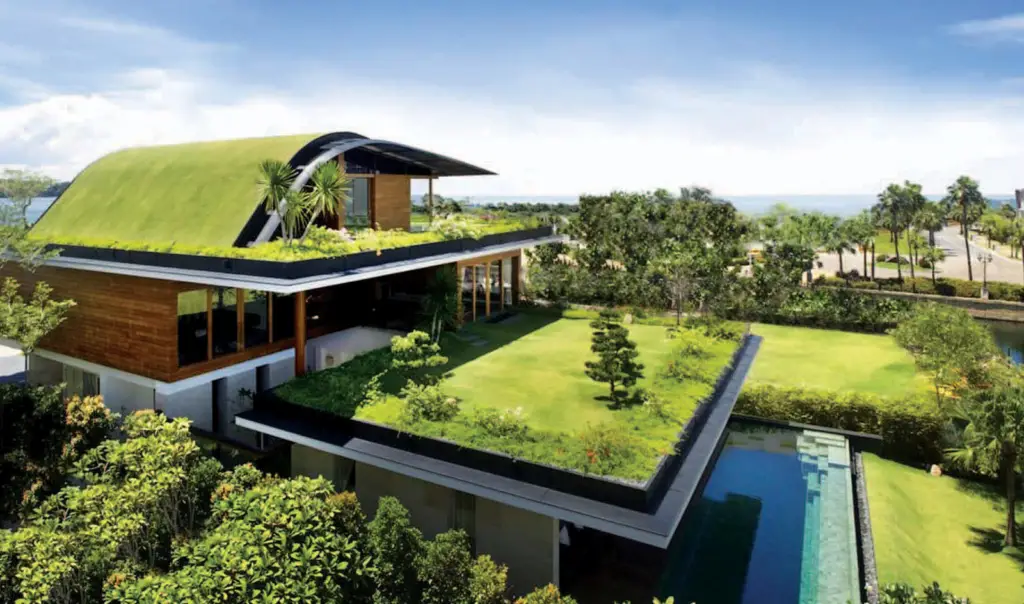

To protect our ecosystem and lessen our carbon footprint, architects are learning new sustainable design techniques for both home and commercial buildings. As a result, green building is becoming more popular in recent times.
According to Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), green building has to do with efficiently making structures using eco-friendly methods and resources. This is done throughout the life cycle of a building.
In this blog post, we will go over the components of green building, as well as the benefits. Let’s dive right in.
The Concept Of Green Building
Green building, also known as sustainable building, is a way of designing and building structures that are eco-friendly. It refers to using environmentally friendly and resource-efficient processes throughout a building’s life cycle. That’s from planning to design, construction, operation, maintenance, renovation, and even demolition.
A structure is termed a green building when it has the following characteristics.
- Use of materials that are sourced sustainably, renewable and recycled.
- Uses technologies that save energy.
- Eco-friendly building materials are utilized.
7 Components Of A Green Building
For a structure to be termed a green building, it should have the following features:
1. Environmentally Preferable Building Materials and Specifications
Every green building must follow the green specifications. This includes specific conditions that property developers, designers, and builders must meet to show that they are practicing sustainable development.
Homeowners and organizations are becoming aware of how toxic chemicals are used in buildings and the health risks they pose. This has put pressure on builders to become more environmentally friendly.
Hence the need to use non-toxic, eco-friendly products for floors, walls, ceilings, windows, paint, insulation, etc.
Key issues like ozone depletion, climate change, fossil fuels, toxic emissions, pollution, waste, mining and mineral extraction, and water use are used to measure how each material affects the environment.
The details of green specifications are not set in stone. That is why for a building to be sustainable, it needs to use materials that improve energy efficiency, reduce waste, save natural resources, and have a long life span.
2. Energy-Efficient
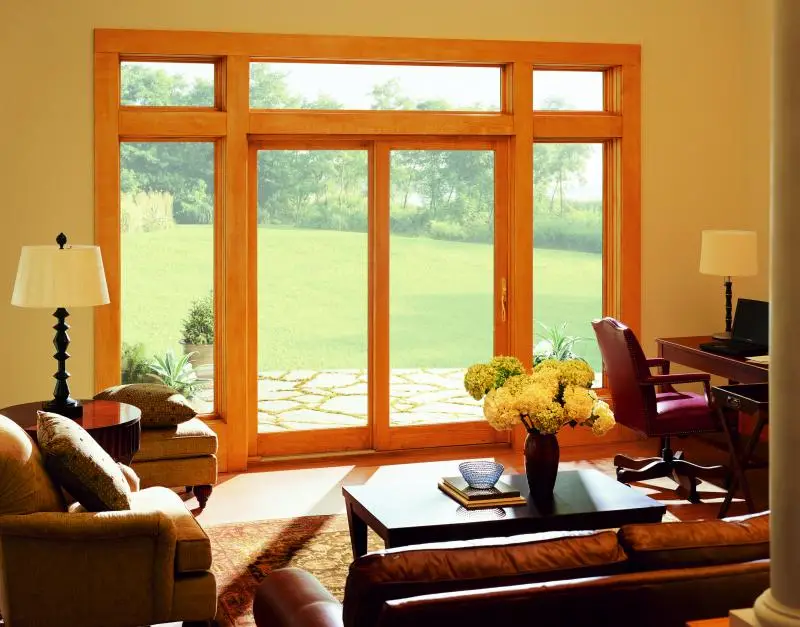

Doors and windows are an important part of green building design. Most of a building’s energy goes in and out through its windows. And an average home can lose 30% of its heat or air conditioning through the windows.
But with smart design and new technology, they can be used to heat, cool, and light the space inside for a better interior.
Below are the different ways windows contribute to a building’s energy efficiency.
a. Glass
The type of glass used in a window greatly affects how well it keeps heat in or out. Low-E glass, also known as low emissivity, is one of the most common types of glass that helps save energy.
It has a special coating that keeps heat from passing through it. This helps keep the temperature inside more stable and saves money on energy bills.
b. Frames
Window frames are made from materials like steel, wood, fiberglass, vinyl, etc. Some of the best energy-efficient windows are made of steel.
c. Seals
Even if your windows’ glass, glazing, and frames are energy-efficient, it’s not enough if air can still get through the spaces around them. So, it’s important to ensure no air leaks around windows.
Furthermore, green buildings’ heating and cooling bills are reduced because it uses solar. Using natural light to design a building saves money on electricity and makes people healthier and more productive.
Green buildings equally have lighting and appliances that use less energy and renewable energy technologies like solar panels and wind turbines.
3. Green Roof
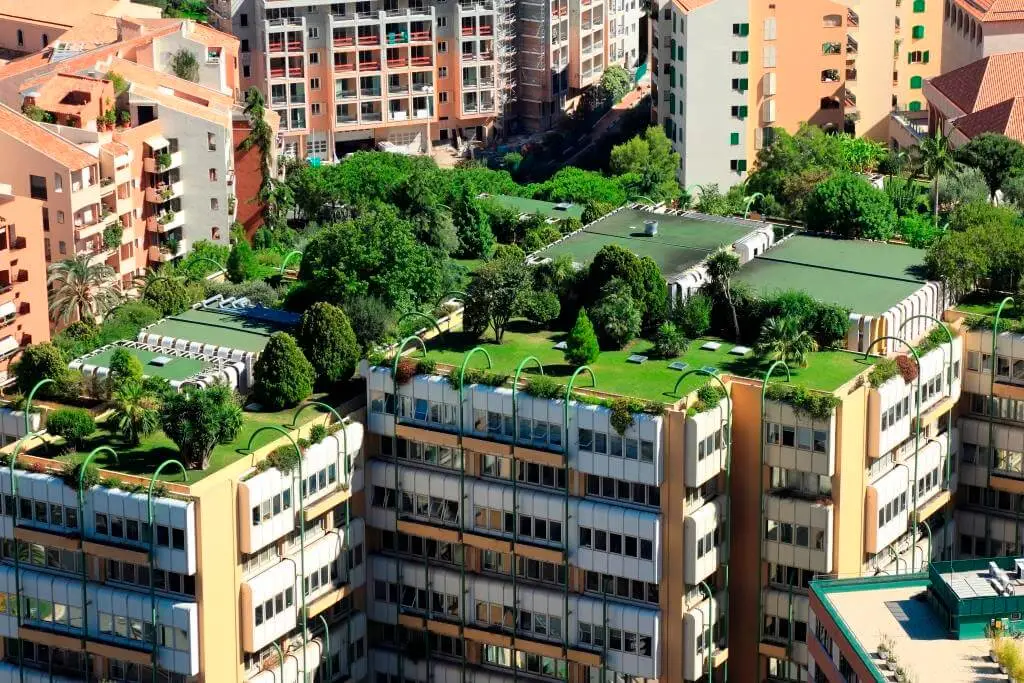

A green roof, also called a rooftop garden, is a layer of plants that grows on top of a roof. Green roofs provide shade, reduce heat, and cool the roof surface and the environment.
The heat island effect can be lessened by putting green roofs on buildings in the cities. Temperatures on green roofs can be 30–40°F lower than those on regular roofs, and the city can cool off by 5°F.
Also, green roofs save 0.7% of a building’s energy use compared to traditional roofs. This lowers peak electricity demand and annually saves $0.23 per square foot of roof surface.
Green roofs are becoming very common because they improve a home’s insulation and lessen the heat lost through the roof. They also a natural habitat for animals and lessen stormwater runoff.
Also read: How Green Spaces Improve Health
4. Water Efficiency in green building
One of the main goals of green buildings is to save water. Water efficiency involves the smart use of our water resources by using technologies that save water.
This includes using ultra-low flush toilets, low-flow shower heads, xeriscaping your landscape, etc. Other include collecting rainwater, recycling and reusing grey water.
Most times, saving water means saving energy. Green buildings use less water for cleaning, cooling, heating, etc. This means less energy is used, leading to low energy bills.
The Leadership in Engineering and Environmental Design (LEEDS) has provided strategies and standards for water conservation. They are categorized into:
a. Portable water
To protect a clean, reliable water source, LEED discourages potable water use for non-potable uses, such as landscaping or indoor plumbing.
Also read: What Are Green Behaviour Examples?
b. Gray water
Gray water is wastewater that hasn’t been treated nor come in contact with toilet waste. It comes from bathtubs, showers, and wash basins in the bathroom.
What makes gray water important to green building practices is that it can be used for other purposes. For example, it can be used to meet landscaping needs or limit the amount of potable water used in toilets.
c. Blackwater
Blackwater is the opposite of potable and gray water. This is because it’s made up of wastewater from toilets.
It’s important to know that in some states, wastewater from showers, kitchen sinks, and bathtubs is also considered blackwater. Therefore, it expands the definition of blackwater.
Blackwater is not useful until it is treated, which should be done on-site to meet tertiary standards.
d. Process water
Given that it is used in cooling towers, chillers, and boilers, there are no rules about how to process water can be used.
The most important thing about process water is that it uses as little potable water as possible.
5. Waste Reduction In Green building
Recycling is a great strategy to reduce the amount of trash produced in green buildings. It is always a fantastic idea to reuse items.
Some trash is labeled hard to recycle, making it more likely to end up in a landfill or get thrown into the ocean.
The quantity of trash is reduced in green buildings by using materials that are easy to recycle or can be used more than once.
6. Indoor Air Quality
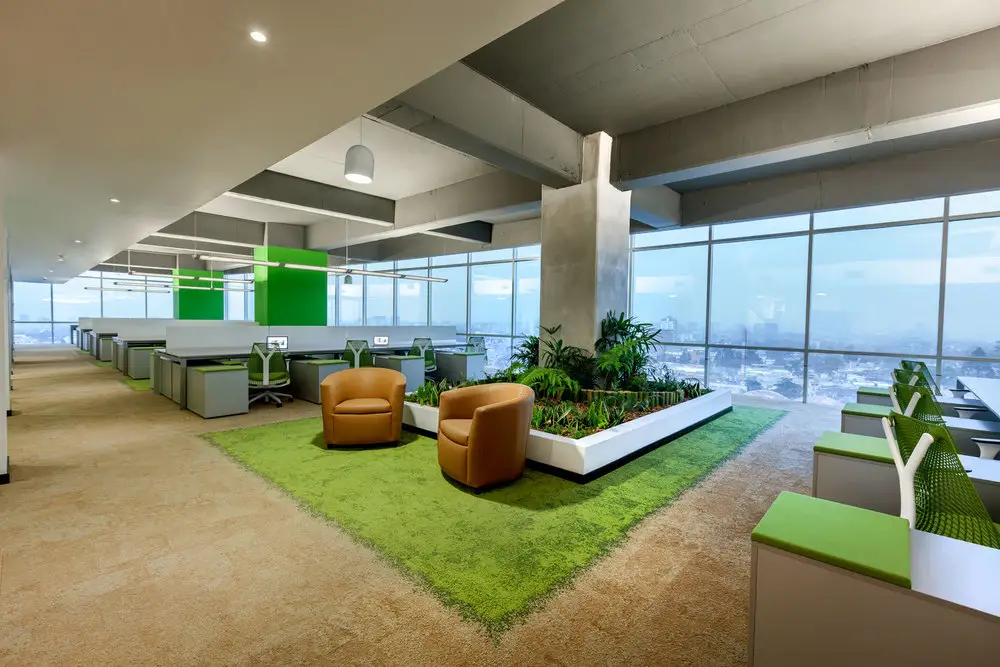

Indoor air quality is an important part of green buildings. It keeps the green technology, building materials, and people inside healthy.
There are a number of things that pollute indoor air quality, like tobacco, cleaning products, the combustion processes in HVAC equipment etc. Getting rid of things like these make improves air quality.
Since dust and other particles that pollute the air hide in materials like carpet, it’s best to choose hardwood flooring instead. And then focus on using paints, coatings, adhesives, and sealants with less Volatile Organic compounds ( VOC).
There should also be restrictions on indoor smoking to keep the air from being polluted. Green buildings have designated smoking areas.
Green buildings are further designed with mechanical ventilation systems to meet the minimum requirements for fresh air so that there is a steady flow of fresh air inside the buildings;
Proper management and maintenance of HVAC systems are very important, from manufacturing, shipping, storing, and fixing to keep dust and other pollutants from building up in the systems.
7. Landscaping

Landscaping is the process of changing a portion of land to make it more useful, valuable, and beautiful. Landscaping includes the art of growing plants to make the landscape area of the property look beautiful.
It can also reduce how much heat a house absorbs. And it can cool the air around a house. Trees and shrubs in the environment act as windbreaks and provide shade. They can also help to filter out pollution from the air.
Why Do Green Building Components Matter?
Green buildings have many benefits. They include:
i. Green Buildings Reduce Pollution
One primary benefit of green building is that it reduces pollution. Facilities account for a sizeable percentage of air pollution, and green buildings reduce emissions using materials that are eco-friendly.
ii. They Are Energy Efficient
Green buildings consume less electricity and produce fewer greenhouse gases than conventional buildings. This has a major effect on climate change.
iii. Green buildings benefit the environment and the people who live inside.
These areas are cozier and healthier, with better air quality and natural light. It also contributes to energy cost savings.
iv. Water Efficiency
It permits water recycling and using alternate water sources by installing specially designed equipment for purification. These advancements safeguard future access to clean water supplies.
v. Reduced Operational Cost And Maintenance
One of the biggest advantages of green buildings is that they require less maintenance. This is a result of carefully planned architectural features that minimize energy consumption and lower energy and water bills for occupants.
vi. They Are Energy Efficient
Buildings that get their energy from natural sources like the sun, wind, and water are very good for the environment. This is because they protect the ecosystem from pollution caused by non-renewable sources such as oil and coal.
vii. It Leads To Carbon Footprint Reduction
Green buildings help reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
viii. They Help Protect Our Ecosystem
By using fewer fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, green building helps in keeping the environment clean.
ix. Quality Of Life
People who live or work in green buildings have reduced stress levels and better health.
Summary
With all the benefits of green buildings mentioned above, it’s the way to go. By using eco-friendly methods and being resource efficient, we enjoy overall improved health. It’s a welcome development in recent times to reduce any negative impact on our environment.
Related posts:
- How Kratom Powder Enhances Gaming Experience? - December 28, 2023
- Green Skills For Youth: Towards A Sustainable World. - August 23, 2023
- Why Brand Consistency in Social Media Graphics is Non-Negotiable - August 22, 2023






2 thoughts on “What Are The 7 Components Of Green Building”