Reviewed by Ogbo Godfrey
The pros of algae biofuel are environmental sustainability, versatility, abundance, etc., while some cons are environmental impact, resource competition, high production costs, etc.
In an era where environmental sustainability has become paramount, the search for alternative energy sources to power our vehicles has gained momentum.
Algae biofuel, often touted as a green solution to our transportation woes, has emerged as a contender in the race to reduce our carbon footprint.
In this article, we delve into the intriguing world of algae biofuel, examining the pros and cons of algae biofuel to provide a comprehensive understanding of its potential for local transportation.
What Is Algae Biofuel?
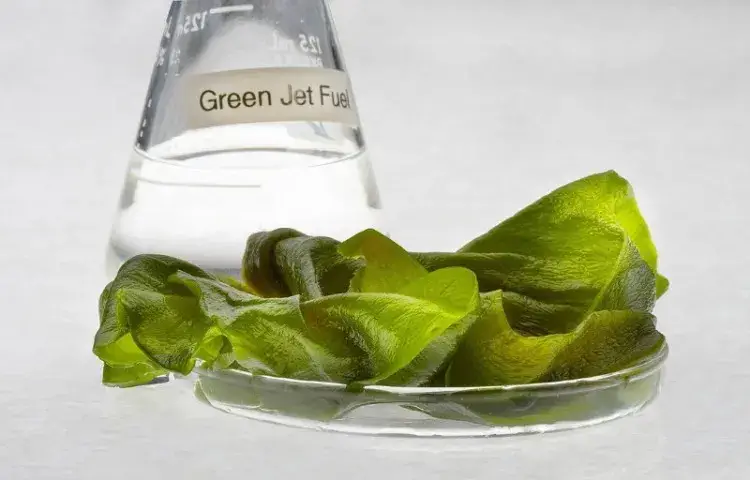

Algae biofuel is a renewable and eco-friendly energy source that harnesses the power of photosynthesis in microalgae to produce fuel.
This innovative biofuel is generated through a process where algae, under the influence of sunlight, convert carbon dioxide and other nutrients into lipids, which can then be refined into biofuels such as biodiesel and bioethanol.
The pros of algae biofuel begins with its environmentally friendly nature. Unlike fossil fuels, algae biofuel produces significantly fewer greenhouse gas emissions, making it a promising contender in the quest to mitigate climate change.
Additionally, algae biofuel is renewable, ensuring a continuous and sustainable energy source for the future. Furthermore, it could reduce our dependence on finite fossil fuels, which are dwindling at an alarming rate.
On the flip side, the cons of algae biofuel are not to be dismissed. One of the significant challenges lies in its production costs, which are currently higher than those of conventional fossil fuels.
Scaling up algae biofuel production to meet local transportation demands presents economic hurdles.
Additionally, the competition for land and resources with food production raises ethical concerns, as cultivating algae for fuel could divert resources away from feeding the world’s population.
Moreover, the cultivation process can be energy-intensive, adding to the overall environmental footprint.
Pros of Algae Biofuel
The pros of algae biofuel are multifaceted, offering a range of benefits that make it an attractive contender in the quest for sustainable transportation solutions.
1. Environmental Sustainability
Algae biofuel is often hailed as an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels. One of its most compelling aspects is its ability to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
When burned, it releases significantly fewer greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2). By considerably lowering carbon dioxide and other pollutants released during combustion, algae biofuel can play a pivotal role in combating climate change.
Algae biofuel shines in the pros of algae biofuel category as a solution for reducing emissions and mitigating environmental impact. This reduction in emissions contributes to combating climate change, making it a vital tool in achieving global carbon reduction goals.
2. Renewable and Abundant
Algae are incredibly prolific, growing rapidly and abundantly in various conditions. Their ability to reproduce quickly means algae biofuel can be produced continuously and sustainably.
Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and non-renewable, algae biofuel offers a long-term solution to our energy needs.
Its renewability highlights the pros of algae biofuel by providing an alternative to depleting fossil fuel reserves.
3. Versatility
Another advantage lies in the versatility of algae as a feedstock source. Unlike some biofuels that compete with food crops for land and resources, algae can be cultivated in a wide range of environments, including wastewater treatment facilities, saline lands unsuitable for traditional agriculture, and even closed-loop systems, minimizing the impact on food production.
4. High Oil Content
Algae are known for their high lipid content, which can be converted into various forms of biofuel, including biodiesel and bioethanol. This increased oil content makes algae an efficient energy source, requiring less land and resources than other biofuel crops like corn or soybeans.
5. Reduced Reliance on Fossil Fuels
As the world grapples with the consequences of fossil fuel depletion and geopolitical instability associated with oil production, algae biofuel offers a potential solution by reducing our reliance on finite fossil fuel reserves.
6. Research and Innovation
Algae biofuel development has spurred innovation and research in biotechnology and renewable energy. These advancements have ripple effects beyond the biofuel industry, leading to breakthroughs in genetics, bioprocessing, and sustainable agriculture.
Cons of Algae Biofuel
While algae biofuel holds tremendous promise, it is not without its share of challenges and drawbacks:
1. High Production Costs
One of the cons of algae biofuel is its high production costs. The cultivation, harvesting, and processing of algae into biofuel can be expensive.
Scaling up production to meet the demands of local transportation can be financially prohibitive, making it less competitive with traditional fossil fuels in the short term.
2. Scalability Issues
Scaling up algae biofuel production to a level that can significantly impact local transportation systems remains a significant hurdle.
The transition from small-scale laboratory settings to large commercial operations is complex, and achieving economies of scale is crucial to making algae biofuel more cost-effective.
3. Resource Competition
A contentious issue that makes it one of the cons of algae biofuel is the competition for resources with food production.
As demand for biofuels grows, there is a risk that large-scale algae cultivation could divert arable land and resources away from food crops. Striking a balance between fuel production and food security is a pressing concern.
4. Energy-Intensive Cultivation
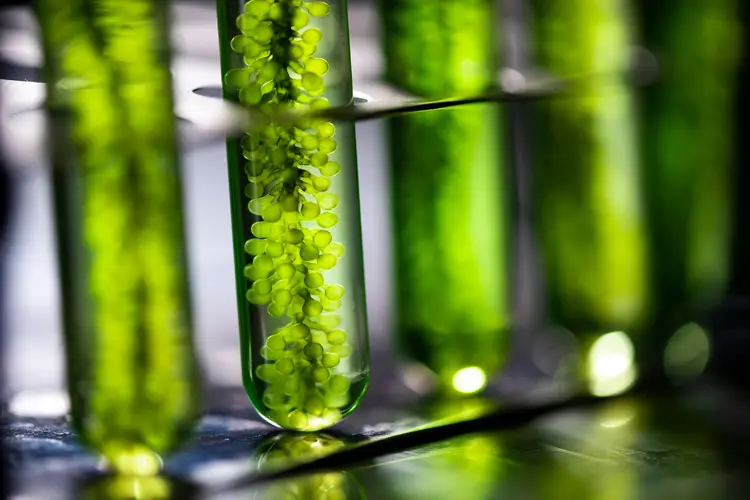

The cultivation of algae can be energy-intensive, particularly in systems that require temperature control, aeration, and nutrient supplementation.
This energy consumption can offset some of the environmental benefits of algae biofuel, as the energy used in its production may come from non-renewable sources.
5. Environmental Impact
While algae biofuel emits fewer greenhouse gases when burned, its production can have environmental impacts. Using fertilizers, water, and land for algae cultivation may lead to habitat disruption and water pollution, primarily if not managed sustainably.
6. Technological Challenges
Algae biofuel production relies on cutting-edge biotechnology and research. Overcoming technical challenges, such as optimizing algae strains for fuel production, requires ongoing innovation and investment.
7. Limited Infrastructure
The infrastructure for algae biofuel production and distribution is still in its infancy. This means that, in many regions, consumers may need more access to algae-based fuels, hindering their adoption of local transportation.
Algae Biofuel in Local Transportation
As we explore the practical applications of algae biofuel, it becomes evident that its potential impact on local transportation is exciting and evolving.
Here, we delve into how algae biofuel is making inroads into the world of vehicles and the key factors shaping its adoption:
1. Success Stories
Algae biofuel has been successfully tested in pilot projects and small-scale initiatives for local transportation. Algae-derived fuels have powered buses, boats, and even airplanes in various parts of the world.
These real-world projects showcase the pros of algae biofuel as a viable alternative to traditional fuels, highlighting its environmental benefits and potential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Government Support and Incentives
Many governments and environmental agencies recognize the importance of sustainable transportation fuels. They have introduced policies and incentives to promote the development and adoption of algae biofuel.
These measures include tax credits, research grants, and mandates for blending biofuels into conventional fuels.
Government support underscores the pros of algae biofuel by creating a favorable environment for its growth in the transportation sector.
3. Technological Advancements
Ongoing research and innovation continue to enhance the efficiency and affordability of algae biofuel production. New strains of algae are being developed to optimize lipid content, and novel cultivation techniques are reducing energy consumption and costs.
These advancements highlight the pros of algae biofuel by addressing some of its inherent limitations, such as production costs and scalability.
4. Environmental Impact
The reduction in greenhouse gas emissions associated with algae biofuel makes it an attractive choice for local transportation systems seeking to reduce their carbon footprint.
This environmental benefit aligns with the global emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly transportation.
The positive environmental impact of algae biofuel reinforces the pros of algae biofuel and its potential contribution to mitigating climate change.
Government Policies and Algae Biofuel
Government policies and incentives significantly influence the growth and adoption of algae biofuel in local transportation.
1. Financial Incentives
Governments worldwide are increasingly offering financial incentives to stimulate algae biofuel development. These incentives include tax credits, grants, and subsidies to researchers, biofuel producers, and consumers.
These measures aim to make algae biofuel more economically competitive with traditional fossil fuels.
2. Biofuel Mandates
Some regions have introduced biofuel blending mandates that require a certain percentage of biofuels, including algae-based fuels, to be mixed with conventional gasoline or diesel.
These mandates help create a market for algae biofuel and drive its production and distribution.
3. Research Grants
Government-funded research grants support scientific studies and innovations in algae biofuel production. These grants enable researchers to explore new technologies, improve algae strains, and develop sustainable cultivation methods.
4. Environmental Regulations
Governments impose environmental regulations and standards on transportation fuels, such as emissions limits. Algae biofuel’s lower greenhouse gas emissions align with these regulations and position it as an environmentally responsible choice for local transportation.
5. Long-Term Sustainability Goals
Many governments have set ambitious sustainability goals, including reducing carbon emissions and transitioning to renewable energy sources. Algae biofuel aligns with these goals, offering a renewable, low-carbon transportation fuel option.
Conclusion
In the journey through algae biofuel and its potential role in local transportation, we’ve examined the pros and cons of algae biofuel in great detail. The future of algae biofuel in local transportation is still unfolding.
As public awareness and demand for sustainable energy solutions grow, algae biofuel’s role may expand, contributing to cleaner and more eco-conscious transportation systems.
Related posts:
- 389 Adjectives Starting with Z (Positive Words and Others) - January 12, 2024
- 389 Adjectives Starting with Y (Positive words and Others) - January 11, 2024
- 389 Adjectives Starting with X (Positive words and Others) - January 10, 2024