The benefits of renewable energy are environmental advantages, economic growth, Technological Innovation, Global Energy Access, etc.
In an era where environmental consciousness takes center stage, understanding the profound benefits of renewable energy sources becomes paramount.
This comprehensive guide aims to unravel the layers of eco-friendly, sustainable energy solutions that not only reduce our carbon footprint but also pave the way for a cleaner, greener tomorrow.
As we embark on this journey, we’ll explore the diverse benefits of renewable energy, from solar and wind to hydro and geothermal. Each source brings its advantages, contributing collectively to a future powered by environmentally conscious choices.
What is Renewable Energy?
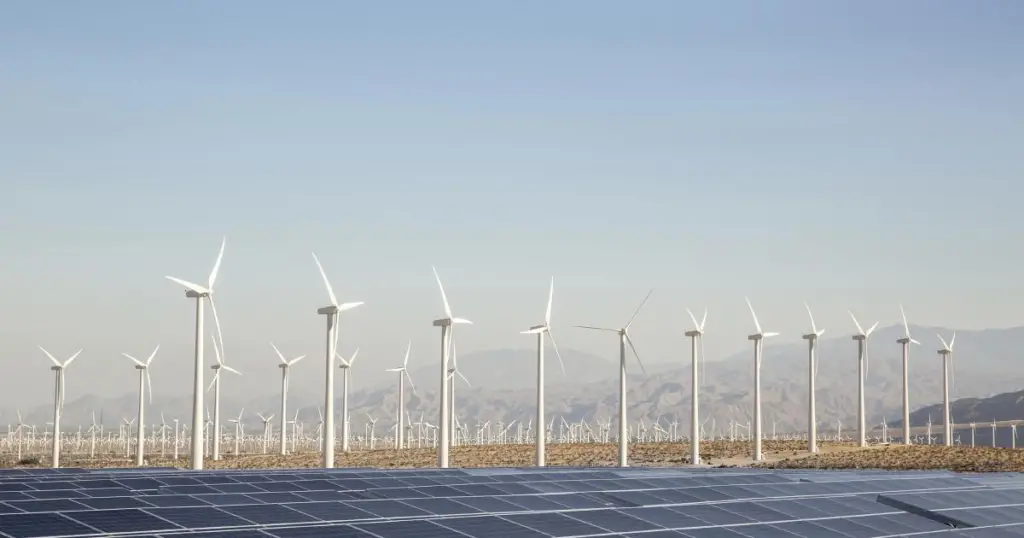

Renewable energy solar is a term encompassing energy derived from virtually inexhaustible and naturally replenishing sources.
Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and contribute to environmental degradation, renewable sources include solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass energy.
The benefits of renewable energy lies in its ability to harness nature’s elements without depleting them, providing a sustainable alternative to conventional energy.
Types of Renewable Energy Sources
Solar Energy
Solar power, a radiant force harnessed from the sun, is a beacon of clean energy, illuminating the present and shaping the future of sustainable power.
In the intricate mosaic of renewable resources, solar power, derived from converting sunlight into electricity, takes center stage as a versatile, abundant, and eco-friendly solution.
At its core are photovoltaic cells, marvels of engineering that directly convert sunlight into electrical power.
These cells, typically made of semiconductor materials like silicon, generate an electric current when exposed to sunlight. When interconnected in solar panels and strategically deployed in arrays, these cells become the building blocks of solar power systems that capture, convert, and channel the sun’s energy into usable electricity.
The benefits of solar energy are manifold. Solar power has its advantages, such as its decentralized nature empowering individuals, businesses, and communities to generate electricity, reducing dependence on centralized grids.
Solar panels on rooftops, solar farms spanning vast landscapes, and even innovative solar roadways exemplify the adaptability and versatility of solar power applications. This has helped multiple farms, including my parents, to flourish without harming the environment.
Furthermore, solar power contributes significantly to environmental sustainability by producing electricity without emitting harmful pollutants or greenhouse gases.
This characteristic aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and reduce the carbon footprint associated with traditional energy sources.
Despite its promising attributes, solar power faces challenges related to intermittency, energy storage, and upfront costs.
Ongoing advancements in battery technology, smart grid integration, and policy support aim to address these challenges, propelling solar power into a leading role in the global transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy landscape.
Wind Energy
Wind turbines capture the kinetic energy of the wind, transforming it into electrical power. Onshore and offshore wind farms contribute significantly to the benefits of renewable energy.
Wind power stands as a formidable force in the renewable energy landscape, tapping into the kinetic energy of the wind to generate electricity.
Unlike traditional power sources, wind power is a sustainable solution that doesn’t deplete finite resources or contribute to harmful emissions.
Wind turbines, the iconic symbols of wind power, are more than just towering structures on the horizon. They capture the wind’s energy with aerodynamic blades connected to a rotor.
As the wind turns the blades, the rotor spins, converting the kinetic energy into electricity through a generator. It’s a mesmerizing interplay between nature and technology, where the breeze transforms into a powerful source of clean energy.
One of the critical advantages of wind power is its scalability. Wind farms can range from small installations to vast fields of turbines, harnessing energy from the gentlest breezes to the strongest gusts.
This adaptability makes wind power a versatile and accessible option for regions worldwide, contributing to a decentralized and diversified energy landscape.
Despite its environmental benefits, wind power has challenges. Concerns about noise, visual impact, and potential harm to wildlife have sparked community debates.
However, ongoing advancements in turbine design and placement strategies aim to address these concerns, ensuring that the transition to wind power is as harmonious as possible.
Hydropower
Hydropower, a timeless and reliable energy source, harnesses the force of flowing water to generate electricity.
This renewable energy method has deep historical roots, dating back to ancient water wheels, and continues to play a pivotal role in our modern quest for sustainable power.
At its core, hydropower operates on a straightforward principle—falling or flowing water possesses kinetic energy, and by capturing this energy, we can convert it into electricity.
Hydroelectric power plants are the engines of this process, strategically positioned along rivers and streams to leverage the natural water flow.
One of the notable advantages of hydropower, such as hydropower, lies in its consistency.
Unlike renewable sources that rely on variable factors like sunlight or wind, flowing water provides a steady and reliable energy source. This reliability makes hydropower a valuable contributor to baseload power, supporting a stable and continuous electricity supply.
Large-scale hydroelectric dams, such as the iconic Hoover Dam, exemplify the magnitude of energy that can be harnessed from flowing water.
These feats of engineering not only generate substantial electricity but also serve purposes like flood control and water storage.
However, the implementation of hydropower is challenging. Environmental concerns, mainly related to the impact on aquatic ecosystems and displacement of communities due to dam construction, underscore the need for thoughtful planning and sustainable practices in hydropower projects.
Geothermal Energy
Beneath the Earth’s surface lies a heat reservoir awaiting harnessing—geothermal energy, a silent yet powerful contributor to our renewable energy portfolio.
Unlike the intermittent nature of some renewable sources, geothermal energy provides a consistent and reliable power source by tapping into the Earth’s internal heat.
The process begins by drilling wells into the Earth, reaching down to where the temperature rises significantly. This depth, known as the geothermal reservoir, contains hot water and steam. When brought to the surface, this high-pressure steam can turn turbines connected to generators, producing electricity.
Geothermal power plants come in various types, including dry steam, flash steam, and binary cycle plants. Each utilizes the Earth’s heat in different ways to generate electricity, making geothermal energy a versatile and adaptable solution.
A significant advantage of geothermal energy is that it doesn’t have much environmental effect. Unlike fossil fuels, geothermal power plants produce negligible greenhouse gas emissions.
Additionally, the footprint of geothermal facilities is relatively small, contributing to a less intrusive energy infrastructure.
Geothermal energy isn’t limited to large power plants; it can be harnessed on a smaller scale for direct-use applications.
Geothermal heat pumps, for example, leverage the Earth’s stable temperatures near the surface to heat efficiently and cool buildings, offering a sustainable solution for residential and commercial spaces.
While geothermal energy is a promising contributor to our sustainable energy future, its widespread adoption faces challenges related to resource availability and geographical limitations.
As technology advances and our understanding of geothermal reservoirs deepens, the potential for harnessing Earth’s inner heat expands, paving the way for a future where clean and reliable energy emerges from the depths below.
Biomass Energy
Biomass, a versatile and renewable energy source, taps into the inherent energy stored in organic materials.
From agricultural residues to wood waste, biomass encompasses a diverse range of biological substances, offering a sustainable solution to our energy needs while addressing waste management challenges.
At its core, biomass energy results from photosynthesis—a natural process where plants capture sunlight and convert it into chemical energy. When these plants, or organic materials derived from them, are burned or processed, the stored energy is released through heat or electricity.
As one of the benefits of renewable energy, the critical advantages of biomass is its status as a carbon-neutral energy source.
While burning biomass releases carbon dioxide, this carbon is part of the natural carbon cycle. Plants absorb carbon dioxide during growth, creating a closed loop where the carbon emitted during combustion is balanced by the carbon absorbed during the biomass’s life cycle.
Wood pellets, agricultural residues, and organic waste are common forms of biomass used for energy production. These materials can be combusted directly, converted into biofuels like ethanol, or utilized in advanced technologies like anaerobic digestion to produce biogas.
The versatility of biomass allows it to be integrated into existing energy infrastructure, providing a renewable alternative to fossil fuels.
However, the widespread adoption of biomass raises questions about land use, resource competition, and the overall sustainability of feedstock production.
Responsible practices are essential to ensuring the environmental benefits of biomass, such as utilizing waste materials and implementing efficient biomass cultivation.
Biofuel
Biofuels, heralded as the green alternative in transportation, represent a significant stride towards reducing the carbon footprint associated with traditional fossil fuels. Derived from organic materials, biofuels offer a cleaner and renewable option for powering vehicles, planes, and ships.
Ethanol and biodiesel are among the most common types of biofuels. Ethanol, often produced from crops like corn or sugarcane, can be blended with gasoline to create a biofuel suitable for traditional combustion engines.
Biodiesel, derived from vegetable oils or animal fats, is a renewable substitute for conventional diesel fuel.
One of the critical advantages of biofuels is their potential to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions.
While combustion releases carbon dioxide, the plants that produce biofuels absorb an equivalent amount of carbon dioxide during their growth, creating a closed carbon cycle. This balance distinguishes biofuels from conventional fossil fuels, which introduce additional carbon into the atmosphere.
The versatility of biofuels extends beyond their use in internal combustion engines. Aviation biofuels, derived from feedstocks like algae or plant oils, are gaining traction as a cleaner alternative for the aviation industry.
Similarly, biofuels can power maritime transport, offering a sustainable option for reducing ship emissions.
However, challenges persist in the widespread adoption of biofuels. Competing land use, potential impacts on food production, and the efficiency of production processes remain areas that necessitate careful consideration and continued innovation.
Benefits of Renewable Energy
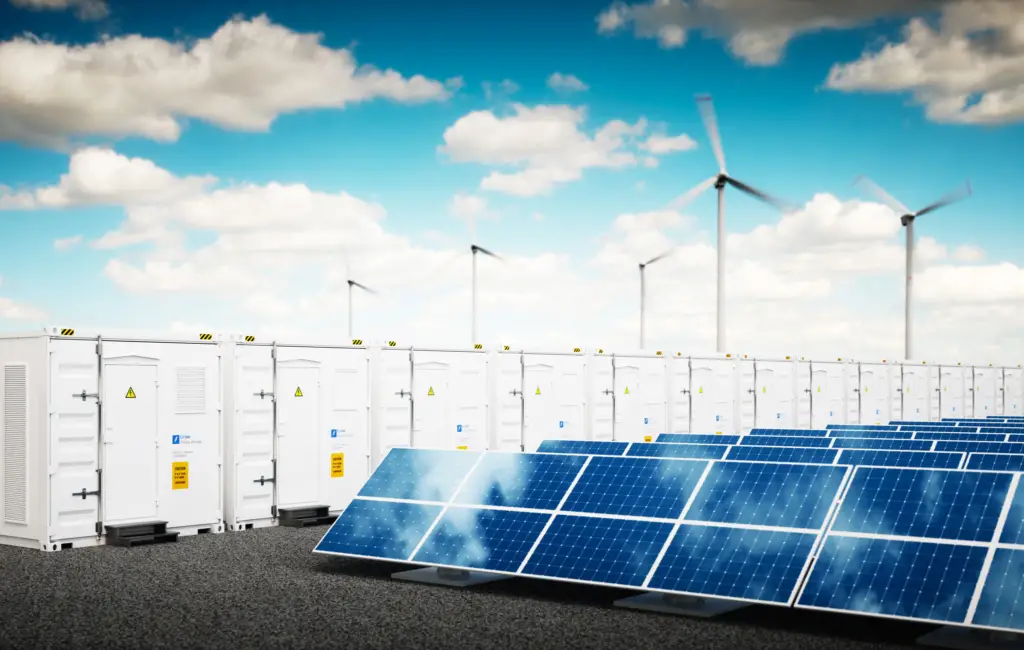

The transition to renewable energy offers many benefits, positioning it as a cornerstone of sustainable development.
1. Environmental Advantages
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
- Mitigates climate change.
- Limits air and water pollution associated with conventional energy sources.
2. Economic Growth
- Fosters job creation in the renewable energy sector.
- Enhances energy security by diversifying the energy mix.
3. Resource Sustainability
- Utilizes inexhaustible natural resources.
- Ensures long-term availability.
- Minimizes dependence on finite and depleting fossil fuels.
4. Technological Innovation
- Drives research and development in clean energy technologies.
- Spurs innovation in energy storage and grid management.
5. Global Energy Access
- Provides energy solutions in remote or off-grid areas.
- Bridges the energy divide by making electricity accessible to all.
6. Health Benefits
- Reduces health risks associated with air and water pollution.
- Improves public health outcomes by transitioning away from fossil fuels.
7. Resilience to Climate Change
- Enhances resilience against the impacts of climate change.
- Mitigates risks associated with extreme weather events and natural disasters.
Disadvantages of Renewable Energy
While there are numerous benefits of renewable energy, it’s essential to acknowledge and address its limitations.
1. Intermittency and Reliability
- Variability in energy production from solar and wind sources.
- Challenges in ensuring a consistent power supply without effective storage solutions.
2. High Initial Costs
- Upfront costs for installing renewable energy infrastructure.
- Long payback periods, although decreasing with advancing technology.
3. Land Use and Aesthetics
- Large-scale solar and wind farms require substantial land.
- Aesthetic concerns and land use conflicts in some regions.
4. Environmental Impact
- Impact on local ecosystems during the construction and maintenance of renewable projects.
- Potential issues with the disposal of solar panels and wind turbine blades.
5. Technological Limitations
- Current limitations in energy storage technology.
- Geographical constraints for specific renewable sources.
6. Transition Challenges
- Integration challenges into existing energy infrastructures.
- Economic and political barriers to a rapid transition.
7. Energy Return
Some renewable technologies have a lower Energy Return On Investment (EROI) compared to conventional sources, which is the energy required to manufacture and install renewable systems.
What is the Best Type of Renewable Energy Source?
Selecting the most suitable renewable energy source depends on various factors, including geographical location, energy needs, and environmental considerations.
1. Location-Specific Factors
- Assess the availability of solar radiation, wind speed, and hydro resources.
- Consider the geological features of geothermal energy.
2. Energy Requirements
- Match the energy source to the scale of energy demand.
- Utilize a combination of sources for a diversified and reliable supply.
3. Environmental Impact
- Evaluate the environmental footprint of each renewable source.
- Opt for technologies with minimal impact on local ecosystems.
4. Technological Advancements
- Stay informed about emerging technologies and improvements.
- Consider the scalability and efficiency of different energy solutions.
5. Economic Viability
- Analyze the cost-effectiveness of implementing specific renewable technologies.
- Explore government incentives and subsidies for support.
6. Community Engagement
- Involve local communities in decision-making processes.
- Address concerns and ensure acceptance of the benefits of renewable energy.
While there is no one-size-fits-all solution, a thoughtful and context-specific approach is crucial in determining the best renewable energy source for a particular setting.
Places Where Renewable Energy is Used the Most
Various countries are discovering the benefits of renewable energy and its is being used widely. The adoption of renewable energy varies globally, with certain regions leading in sustainable practices and investment.
1. Scandinavian Countries
Denmark and Sweden excel in wind energy, with a significant share of their electricity coming from wind farms. When I went to Copenhagen, I noticed several wind turbines. It’s great that they’re utilizing it efficiently.
Norway also uses hydropower extensively, benefiting from its abundant water resources.
2. Germany
A pioneer in solar energy, Germany has established itself as a leader in solar photovoltaic technology. The country’s commitment to the “Energiewende” (energy transition) has led to substantial investments in renewable infrastructure and reduced carbon emissions.
3. China
As the world’s largest emitter of greenhouse gases, China has been actively investing in renewable energy to address environmental concerns. The country leads globally in solar panel production and is making significant strides in wind energy development.
4. United States
Various states in the U.S., such as California and Texas, have embraced renewable energy. California, in particular, has been a trailblazer in solar energy implementation, with a strong emphasis on reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
5. Iceland
With its abundant geothermal resources, Iceland relies heavily on geothermal power for heating and electricity. The country’s commitment to renewable energy has positioned it as a model for geothermal utilization.
6. India
India has set ambitious renewable energy targets and has made substantial progress, especially in solar power. The country’s focus on decentralized renewable energy solutions aims to provide energy access to remote and rural areas.
7. South Africa
South Africa has made significant strides in integrating renewable energy into its energy mix, mainly focusing on wind and solar projects. These initiatives contribute to energy diversification and environmental sustainability.
8. Brazil
Known for its extensive use of hydropower, Brazil has harnessed the energy potential of its rivers for electricity generation. The country’s commitment to renewable sources aligns with its efforts to reduce deforestation and mitigate environmental impact.
Understanding the global landscape of renewable energy adoption helps identify successful models and strategies for implementation in different regions.
Local factors, policy frameworks, and public engagement play crucial roles in determining the success of renewable energy initiatives.
Can Renewable Energy Run Out?
One of the benefits of renewable energy is that they are considered sustainable and nearly inexhaustible. Unlike finite fossil fuels, renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydro are continually replenished by natural processes.
However, it’s essential to consider specific factors that can influence the availability and effectiveness of renewable energy.
Resource Variability
Solar and wind energy are subject to natural variations based on weather conditions. Cloud cover, nighttime, and calm days can temporarily limit the availability of these resources.
Hydrological Changes
Changes in precipitation patterns and water availability can impact hydropower generation. Droughts or alterations in river flow can affect the reliability of hydroelectric power.
Geographic Constraints
Geothermal energy is abundant in regions with tectonic activity but not universally accessible. Areas with limited geothermal resources may need more support in geothermal power generation.
Biomass Sustainability
Sustainable biomass energy relies on responsible forestry and agriculture practices. Overexploitation or mismanagement of biomass resources can lead to depletion.
Technological Advances
Continued technological advancements may enhance the efficiency of harnessing renewable energy, ensuring better utilization of available resources.
Conclusion
The benefits of renewable energy sources extend far beyond environmental responsibility. Embracing these sustainable alternatives not only mitigates the impact of climate change but also ushers in a new era of energy independence and innovation.
As we adopt eco-friendly practices and invest in renewable technologies, we sow the seeds for a future where clean energy isn’t just an option but a necessity. Let this guide serve as a roadmap toward a world where the benefits of renewable energy propel us into a brighter, more sustainable future.
Related posts:
- 389 Adjectives Starting with Z (Positive Words and Others) - January 12, 2024
- 389 Adjectives Starting with Y (Positive words and Others) - January 11, 2024
- 389 Adjectives Starting with X (Positive words and Others) - January 10, 2024