In the past few years, the world’s reliance on fossil fuels has become a bigger problem from an environmental, supply, and geopolitical point of view. Many countries are trying to cut back on their use of fossil fuels to fight these problems.
An electric vehicle has become a big new trend in the transportation field. Because of this, sales of electric vehicles (EVs) have increased in the last ten years.
Only 120,000 electric cars were sold around the world in 2012. In 2022, though, more than that has been sold in the first quarter of the year. Even though this growth in electric transportation already saves about 1.5 million barrels of oil per day, it also greatly increases the need for electricity.
At the same time, sustainably making enough electricity is hard. Most of an EV’s effect on the environment comes from how it is made and how electricity is made to power it.
Because of this, it is very important to increase the production of renewable energy, and solar power is one of the most popular ways to do this at home.
This article will tell you nine things you need to know about charging your Electric car with solar. Keep reading.
You may like: Are Electric Cars Really Green?
Can you charge your EV with solar?
In short, yes, you can charge your EV with solar and don’t even need smart charging features to do it. One of the best things about having rooftop solar is being able to charge an electric vehicle (EV) with your power.
If you charge your EV with electricity from your solar panels, you don’t have to pay for “fuel” anymore. In reality, though, this is more complex than it sounds.
In this article, we talk about the available home EV chargers, look at the different solar charging options, figure out how long it will take to charge an EV using solar etc.

1. How solar energy and EV charging works?
It is possible to easily charge an electric vehicle (EV) using solar panels on your roof, but it relies on a number of factors, such as the size of your solar system, the time of day, and the weather. You will need a large enough solar system plus assistance from a smart charger, which we’ll cover later if you solely want to utilize solar to charge your EV.
The following factors determine how simple it is to charge an electric vehicle (EV) with solar energy:
- Charger type: Charger speeds can be anywhere from 2kW to 22kW
- How big is your solar system? Most solar systems on rooftops are between 5kW and 15kW.
- How much do you need to charge the battery of the car?
- How often do you go places, and how far do you drive?
This may sound hard, but there’s a free solar calculator with a built-in EV charging simulator to estimate how much solar you need to charge an EV based on how far you drive and what kind of charger you have.
If you don’t drive much, you can easily charge your EV at home with solar power using a simple plug-in (level 1) charger and a small (5kW) solar system.
The problem is that when it’s cloudy or rainy, the solar system needs to make more power to run a level 2 charger at full power. Luckily, smart EV chargers can help with this, as can several other solar charging options explained below.
2. EV battery capacity: Kilowatt-hours (KWh)
It is crucial to understand how much and how far an EV battery can store energy before discussing the various charger types and their charging rates.
Electric cars can have batteries ranging in capacity from 24 kWh to 100 kWh or more. Batteries are measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
Most EVs have batteries that can hold about 65 kWh, which gives them a range of about 350 km, depending on the weather and how well you drive.
Your range will be between 5 and 8 kilometers for each kWh of battery capacity. While bigger, high-performance EVs can consume 20kWh or more every 100km of driving (1kWh = 5km), lighter, more efficient EVs can use as low as 12kWh per 100km (1kWh = 8.2km).
On average, EVs use around 16kWh per 100km (1.0kWh = 6.0km).
3. Home Options for Charging an EV
When someone with solar on their roof buys an electric vehicle, they first think about how to charge it and if it will work with their solar system.
The majority of level 2 chargers, often known as “wallbox chargers,” are straightforward devices that can be put on any house or establishment, whether or not it has rooftop solar. This is crucial to remember before we get into the specifics.
Finding out if your utility grid connection has enough extra power to handle a level 2 charger, which typically requires a 32A supply, is the major challenge.
There are technically three levels of EV chargers, but you can only use the first two at home. Level 1 is a simple portable charger plugged into any standard 10A power outlet.
Most EVs come with these basic chargers as standard equipment. Level 2 chargers are small and attached to the wall.
They are installed permanently in homes and businesses. Level 3 chargers are big, powerful, and fast. They are usually found at EV charging stations on the side of the road.
- Level 1: 10A or 15A plug-in chargers that you can take with you from 1.4kW to 3.6kW
- Level 2: Chargers that are attached to the wall and range from 5kW to 22kW (Wallbox charger)
- Level 3: 50kW to 300kW EV charging stations on the side of the road (DC fast charger)
4. The different Types of Home EV Chargers
There are four types of home Ev chargers. They are:
- Portable plug-in chargers: 1.4kW to 3.6kW (Level 1)
- Single-phase Wallbox EV chargers with 3.3kW to 7.4kW (Level 2)
- Three-phase Wallbox EV chargers, from 7.0kW to 22.0kW (Level 2)
- Combined Solar inverter and EV charger, 5.0kW to 7.4kW (Level 2)

Let’s examine these EV chargers one after the other.
1. Portable plug-in chargers:
Most EVs come with a straightforward level 1 charger that works with any standard 10A wall outlet.
Depending on the battery size and beginning state of charge, these tiny portable chargers often take 24 to 36 hours to recharge an average EV fully.
The majority of 10A chargers can charge at a maximum rate of 2.2kW, although they often draw between 1.7kW and 2.0kW, adding between 10km and 14km of range per hour, depending on the car.
Although more potent 15A plug-in chargers are also available, installing a dedicated 15A outlet is usually necessary.
Solar EV charging with a 10A level 1 plug-in socket charger is relatively simple because an average home 6kW solar system can output 2 to 3kW even during partially overcast weather.
2. Single-phase Wallbox EV chargers:
Many different options and designs are available for Level 2 single-phase EV chargers, which can be placed on walls or posts.
Most are rated at 32 Amp, which is 7.4kW of power and may give a car a range of 40 to 50 kilometers per hour when charging at its maximum pace.
A daily vehicle recharge should only take an hour or two, given that the average individual drives less than 50 kilometers. Using a standard single-phase 7kW Wallbox charger, an average EV may be fully recharged in 8 to 10 hours.
3. Three-phase Wallbox EV chargers:
Home Level 2 three-phase EV chargers typically have a 32 Amp rating and resemble single-phase wall-mounted equipment in appearance.
The three supply phases, however, allow them to offer three times as much power as the single-phase version, or around 22 kW of charging power.
This may provide a car with a range of 120 to 150 kilometers per hour at the highest charge rate. Using a 3-phase Wallbox charger, an average EV may be fully recharged in less than 3 hours.
4. Combined Solar inverter and EV charger:
A recent technological advancement is a solar inverter and electric vehicle charger that can charge directly from rooftop solar.
A creative approach that removes the need for a separate EV charger, additional cabling, and prospective electrical improvements is to integrate a charger with a solar inverter. The inverter must be located near or in a garage, which is the sole drawback.
SolarEdge is the first solar inverter producer to create a hybrid solar inverter and EV charger that can charge up to 7.4kW from solar power alone or solar power and the grid simultaneously.
This is perfect for those who want smart home automation and want to add solar and an EV charger at the same time.
You should note that the SolarEdge energy meter can only use the smart charging functions.
5. How long it takes solar energy to charge an EV?
This is a vague question because it depends on the EV battery’s size and the solar system’s size. Most of the time, a standard 6.5kW rooftop solar system will need a long sunny day to charge an average EV from 20% to 80%.
When it comes to charging an EV at home, it makes sense that the more solar power you have, the better, especially in colder, less sunny places.
If you don’t drive more than 80 km daily, it will be easy to charge your EV with a regular rooftop solar system as long as you are home during the day. Use solar and EV charging calculators to see what it would be like to charge an EV with the sun.
How low the EV battery is, the type of EV charger and the weather can greatly affect how long it takes to charge. On a sunny day, an EV could be charged up to 80% with a larger 10kW rooftop solar array and a more powerful 7kW Type 2 charger.
A more powerful 3-phase charger and a 15kW rooftop solar array could do it in as little as 5 hours. Many of these charging times are based on the idea that the household load is low and the weather is mostly sunny.
This is only sometimes the case, though. If you want to avoid paying for grid power to charge your EV at home, a smart EV charger can help.
EV CHARGING TIMES ON AVERAGE PER DAY WITH A SOLAR SYSTEM:
A 6.5kW solar system takes 7 hours to charge a 64kWh Hyundai Kona from 20% to 80%.
With a 10kW solar system, it takes 5 hours to charge a 64kWh Hyundai Kona from 20% to
80%.
6. EV Charging Efficiency
The efficiency of charging a typical EV with a home EV charger depends on several things, such as the charge rate, the ambient temperature, the temperature of the battery, the length of the charging cable, and how well the vehicle’s power conversion system works (AC to DC converter).
Because of several things, the temperature can greatly affect how well a charger works. When it’s very hot outside, a car may need to run the battery cooling system while it’s charging, and when it’s very cold outside, the battery heating system needs to be running while the car is charging.
Due to increased electrical resistance, any charger will work less well when the temperature is very high. Clean Energy Reviews recently used a BYD Atto 3 electric vehicle to compare how well a small portable 10A charger and a 7kW dedicated EV charger charged the car at different rates.
7. Smart chargers for EVs

Smart EV chargers have different smart charging modes that let you choose the best time and way to charge your EV.
There are different ways to charge, such as scheduling charging to happen automatically during off-peak hours or when electricity prices are low, boost charging, and solar-only charging.
Use a smart EV charger with solar panels on your roof to get the most out of them. These smart chargers can be controlled by an app and can check how much solar power you have and send it to your EV charger instead of sending it to the power grid.
This way, you won’t have to use power from the grid to charge your EV, even if the weather is bad or if it only works sometimes.
8. How smart chargers for EVs work
Standard home EV chargers use a fixed amount of power, usually between 3.5kW and 7.4kW, depending on the type of charger and how it is set up.
But when charging from solar panels on a roof, the energy produced may be much less, especially when it is cloudy or rainy.
Smart EV chargers get around this problem by putting a CT clamp, an energy metering device, near the main electrical supply connection to track how much energy is going into and out of the grid.
Once it sees that your solar panels are sending extra power to the grid, it will charge the EV at that amount. But this can change all the time because of changes in how much power is used and how much solar power is made, so the smart EV charger constantly changes the charge rate to match the amount of solar power that is made in excess.
9. EV charging with a battery
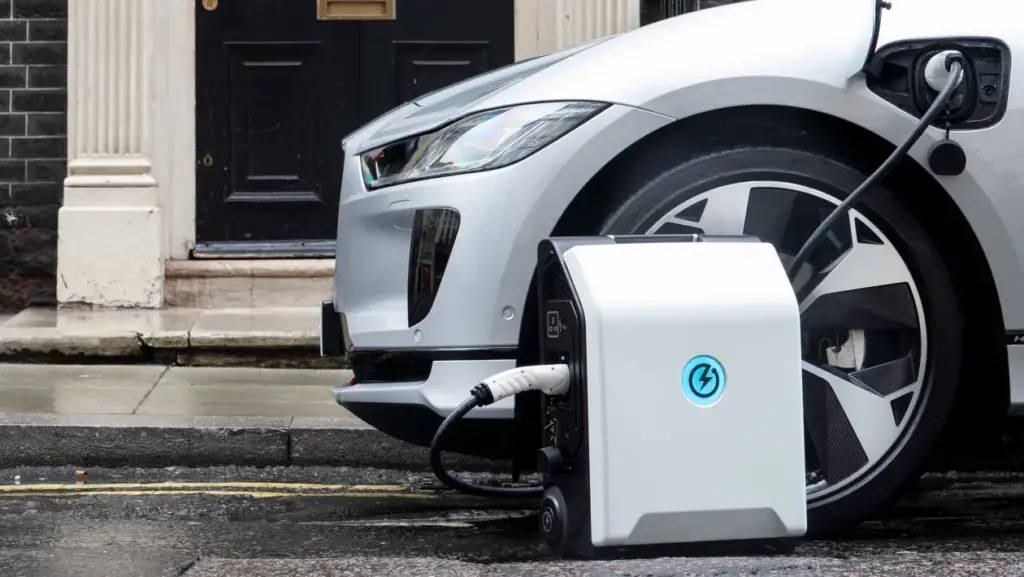

If you are gone most of the day, charging an EV with solar panels on your roof can be hard. But battery storage can help with this. Most home battery systems have a capacity of 10 kWh, giving you up to 80 km of driving range if you can simultaneously charge the whole battery.
You can only use half of the battery because your home needs it, so you can only drive 30 to 40 km. But since most people (especially those who live in cities) only drive short distances on average, this may be fine.
People who drive long distances will need a bigger battery to charge their car during off-peak hours. Smart EV charging systems, like the SolarEdge inverter EV charger, can help you manage and optimize your EV charging by using solar power and battery storage.
Summary
Making the choice to switch from a gasoline or diesel vehicle to an electric vehicle (EV) involves some financial investment and some minor but important driving behavior modifications. Solar integration into the mix is similar; it is not as difficult as it seems and anyone can do it.
Related posts:
- How Kratom Powder Enhances Gaming Experience? - December 28, 2023
- Green Skills For Youth: Towards A Sustainable World. - August 23, 2023
- Why Brand Consistency in Social Media Graphics is Non-Negotiable - August 22, 2023